Human Biomonitoring of Mycotoxins in Blood, Plasma and Serum in Recent Years: A Review
- PMID: 32121036
- PMCID: PMC7150965
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12030147
Human Biomonitoring of Mycotoxins in Blood, Plasma and Serum in Recent Years: A Review
Abstract
This manuscript reviews the state-of-the-art regarding human biological monitoring (HBM) of mycotoxins in plasma serum and blood samples. After a comprehensive and systematic literature review, with a focus on the last five years, several aspects were analyzed and summarized: a) the biomarkers analyzed and their encountered levels, b) the analytical methodologies developed and c) the relationship between biomarker levels and some illnesses. In the literature reviewed, aflatoxin B1-lysine (AFB1-lys) and ochratoxin A (OTA) in plasma and serum were the most widely studied mycotoxin biomarkers for HBM. Regarding analytical methodologies, a clear increase in the development of methods for the simultaneous determination of multiple mycotoxins has been observed. For this purpose, the use of liquid chromatography (LC) methodologies, especially when coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) or high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), has grown. A high percentage of the samples analyzed for OTA or aflatoxin B1 (mostly as AFB1-lys) in the reviewed papers were positive, demonstrating human exposure to mycotoxins. This review confirms the importance of mycotoxin human biomonitoring and highlights the important challenges that should be faced, such as the inclusion of other mycotoxins in HBM programs, the need to increase knowledge of mycotoxin metabolism and toxicokinetics, and the need for reference materials and new methodologies for treating samples. In addition, guidelines are required for analytical method validation, as well as equations to establish the relationship between human fluid levels and mycotoxin intake.
Keywords: HBM; blood; mycotoxins; plasma; serum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


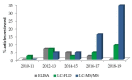

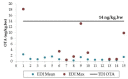
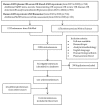
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Exposure to Mycotoxins in Spanish Children through the Analysis of Their Levels in Plasma Samples.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;13(2):150. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020150. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672088 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of multiple mycotoxins in paired plasma and urine samples to assess human exposure in Nanjing, China.Environ Pollut. 2019 May;248:865-873. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.091. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Environ Pollut. 2019. PMID: 30856502
-
Mycotoxins Exposure of French Grain Elevator Workers: Biomonitoring and Airborne Measurements.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 27;13(6):382. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060382. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071776 Free PMC article.
-
Mycotoxins-Biomonitoring and Human Exposure.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 3;13(2):113. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020113. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33546479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Literature review and evaluation of biomarkers, matrices and analytical methods for chemicals selected in the research program Human Biomonitoring for the European Union (HBM4EU).Environ Int. 2022 Nov;169:107458. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107458. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Environ Int. 2022. PMID: 36179646 Review.
Cited by
-
Citrinin Dietary Exposure Assessment Approach through Human Biomonitoring High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Data.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Jun 9;69(22):6330-6338. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01776. Epub 2021 Jun 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34060319 Free PMC article.
-
Predicted Aflatoxin B1 Increase in Europe Due to Climate Change: Actions and Reactions at Global Level.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 20;13(4):292. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040292. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overall Exposure of European Adult Population to Mycotoxins by Statistically Modelled Biomonitoring Data.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Oct 1;13(10):695. doi: 10.3390/toxins13100695. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34678988 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of 19 Mycotoxins in Human Plasma in a Region of Northern Spain.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;12(12):750. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120750. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33261074 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Validation of a Direct Competitive ELISA for Multiple Mycotoxin Detection in Human Serum.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 25;14(11):727. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110727. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sulyok M., Krska R., Schuhmacher R. A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometric multi-mycotoxin method for the quantification of 87 analytes and its application to semi-quantitative screening of moldy food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007;389:1505–1523. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1542-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pulina G., Battacone G., Brambilla G., Cheli F., Danieli P.P., Masoero F., Pietri A., Ronchi B. An Update on the Safety of Foods of Animal Origin and Feeds. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2014;13:3571. doi: 10.4081/ijas.2014.3571. - DOI
-
- Binder E.M. Managing the risk of mycotoxins in modern feed production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007;133:149–166. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2006.08.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

