Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana
- PMID: 32121505
- PMCID: PMC7143859
- DOI: 10.3390/insects11030155
Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana
Abstract
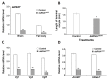
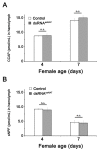
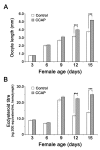
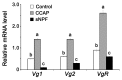
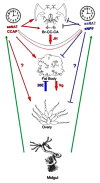
Although the regulation of vitellogenesis in insects has been mainly discussed in terms of 'classical' lipid hormones, juvenile hormone (JH), and 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E), recent data support the notion that this process must be adjusted in harmony with a nutritional input/reservoir and involvement of certain indoleamines and neuropeptides in regulation of such process. This study focuses on crosstalks among these axes, lipid hormones, monoamines, and neuropeptides in regulation of vitellogenesis in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana with novel aspects in the roles of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (aaNAT), a key enzyme in indoleamine metabolism, and the enteroendocrine peptides; crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) and short neuropeptide F (sNPF). Double-stranded RNA against aaNAT (dsRNAaaNAT) was injected into designated-aged females and the effects were monitored including the expressions of aaNAT itself, vitellogenin 1 and 2 (Vg1 and Vg2) and the vitellogenin receptor (VgR) mRNAs, oocyte maturation and changes in the hemolymph peptide concentrations. Effects of peptides application and 20E were also investigated. Injection of dsRNAaaNAT strongly suppressed oocyte maturation, transcription of Vg1, Vg2, VgR, and genes encoding JH acid- and farnesoate O-methyltransferases (JHAMT and FAMeT, respectively) acting in the JH biosynthetic pathway. However, it did not affect hemolymph concentrations of CCAP and sNPF. Injection of CCAP stimulated, while sNPF suppressed oocyte maturation and Vgs/VgR transcription, i.e., acting as allatomedins. Injection of CCAP promoted, while sNPF repressed ecdysteroid (20E) synthesis, particularly at the second step of Vg uptake. 20E also affected the JH biosynthetic pathway and Vg/VgR synthesis. The results revealed that on the course of vitellogenesis, JH- and 20E-mediated regulation occurs downstream to indoleamines- and peptides-mediated regulations. Intricate mutual interactions of these regulatory routes must orchestrate reproduction in this species at the highest potency.
Keywords: 20-hydroxyecdysone; Periplaneta americana; aaNAT; biogenic amines; juvenile hormone; neuropeptides; oocytes; vitellogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 28;8:593613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.593613. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-midgut cross-talk and autocrine metabolastat via the sNPF/CCAP negative feed-back loop in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Dec;362(3):481-96. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2242-4. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 26178071
-
Insulin/IGF signaling and TORC1 promote vitellogenesis via inducing juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the American cockroach.Development. 2020 Oct 23;147(20):dev188805. doi: 10.1242/dev.188805. Development. 2020. PMID: 33097549
-
Involvement of Cis-Acting Elements in Molecular Regulation of JH-Mediated Vitellogenin Gene 2 of Female Periplaneta americana.Front Physiol. 2021 Aug 30;12:723072. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.723072. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34526913 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of female reproduction in mites: a unifying model for the Acari.J Insect Physiol. 2009 Dec;55(12):1079-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.08.007. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Insect Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19698719 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 28;8:593613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.593613. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut symbiotic bacteria enhance reproduction in Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) by regulating juvenile hormone III and 20-hydroxyecdysone pathways.Microbiome. 2025 May 23;13(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40168-025-02121-x. Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40410832 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile Hormone and Ecdysteroids Facilitate the Adult Reproduction Through the Methoprene-Tolerant Gene and Ecdysone Receptor Gene in the Female Spodoptera frugiperda.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 23;26(5):1914. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051914. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076541 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-Mediated Functional Analysis Reveals the Regulation of Oocyte Vitellogenesis by Ecdysone Signaling in Two Coleoptera Species.Biology (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;12(10):1284. doi: 10.3390/biology12101284. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37886994 Free PMC article.
-
Function Analysis of Cholesterol 7-Desaturase in Ovarian Maturation and Molting in Macrobrachium nipponense: Providing Evidence for Reproductive Molting Progress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 8;24(8):6940. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086940. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tufail M., Nagaba Y., Elgendy A.M., Takeda M. Regulation of vitellogenin genes in insects. Entomol. Sci. 2014;17:269–282. doi: 10.1111/ens.12086. - DOI
-
- Elmogy M., Mohamed A.A., Tufail M., Uno T., Takeda M. Molecular and functional characterization of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana, Rab5: The first exopterygotan low molecular weight ovarian GTPase during oogenesis. Insect Sci. 2018;25:751–764. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12485. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raikhel A.S., Browon M.R., Belles X. Hormonal control of reproductive processes. In: Gilbert L.I., Iatrou K., Gill S.S., editors. Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science. Volume 3. Elsevier Pergamon; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2005. pp. 433–491. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

