Nanodiamonds with powerful ability for drug delivery and biomedical applications: Recent updates on in vivo study and patents
- PMID: 32123595
- PMCID: PMC7037532
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2019.09.003
Nanodiamonds with powerful ability for drug delivery and biomedical applications: Recent updates on in vivo study and patents
Abstract
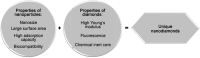
Nanodiamonds are novel nanosized carbon building blocks possessing varied fascinating mechanical, chemical, optical and biological properties, making them significant active moiety carriers for biomedical application. These are known as the most 'captivating' crystals attributed to their chemical inertness and unique properties posing them useful for variety of applications in biomedical era. Alongside, it becomes increasingly important to find, ascertain and circumvent the negative aspects associated with nanodiamonds. Surface modification or functionalization with biological molecules plays a significant role in managing the toxic behavior since nanodiamonds have tailorable surface chemistry. To take advantage of nanodiamond potential in drug delivery, focus has to be laid on its purity, surface chemistry and other considerations which may directly or indirectly affect drug adsorption on nanodiamond and drug release in biological environment. This review emphasizes on the basic properties, synthesis techniques, surface modification techniques, toxicity issues and biomedical applications of nanodiamonds. For the development of nanodiamonds as an effective dosage form, researchers are still engaged in the in-depth study of nanodiamonds and their effect on life interfaces.
Keywords: Biochemical application; Diamondoids; Drug targeting; Nanomedicine; Surface functionalization.
© 2019 Xi'an Jiaotong University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
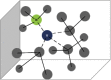
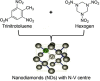



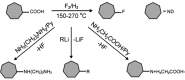
References
-
- Georgakilas V., Perman J.A., Tucek J. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:4744–4822. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary A., Welch J.O., Jackman R.B. Electrical properties of monodispersed detonation nanodiamonds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010;96:242903.
-
- Vul A.Y., Dideikin A.T., Aleksenskii A.E. Royal Society of Chemistry; 2014. Detonation Nanodiamonds: Synthesis, Properties and Applications, RSC Nanosci. Nanotechnol; pp. 37–48.
-
- Tisler J., Balasubramanian G., Naydenov B. Fluorescence and spin properties of defects in single digit nanodiamonds. ACS Nano. 2009;3:1959–1965. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

