Plasma levels of acylated ghrelin in patients with insulinoma and expression of ghrelin and its receptor in insulinomas
- PMID: 32124259
- PMCID: PMC7266859
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-020-02233-4
Plasma levels of acylated ghrelin in patients with insulinoma and expression of ghrelin and its receptor in insulinomas
Abstract
Background: Insulinoma is a subtype of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Many patients with insulinoma are obese due to frequent food intake. Ghrelin is associated with obesity and blood levels of insulin. It is not clear if plasma levels of ghrelin in insulinoma patients correlate with hyperinsulinemia and obesity. Expression of ghrelin and its receptor has not been well demonstrated in insulinoma.
Objective: To study if plasma levels of ghrelin is associated with obesity and hyperinsulinemia or hyperproinsulinemia in patients with insulinoma, and to detect the expression of ghrelin and its receptor in insulinoma.
Methods: Plasma levels of acylated ghrelin, insulin, and proinsulin were measured in 37 patients with insulinoma and 25 controls by ELISA. Expression of ghrelin and its receptor GHS-R1A was examined in 20 insulinoma and paired pancreatic specimens by immunostaining. P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
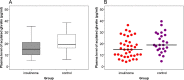
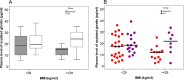
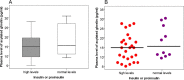
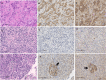
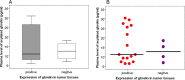
Results: The plasma levels of acylated ghrelin in patients with insulinoma were significantly lower than that in the controls (median 15 pg/ml vs. 19 pg/ml, respectively, P = 0.016). The reduced plasma levels of acylated ghrelin in patients were significantly correlated with obesity, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperproinsulinemia (P = 0.029 and P = 0.028, respectively). Expression of ghrelin and its receptor GHS-R1A was shown in the majority of insulinoma specimens. The expression of GHS-R1A was positively correlated with ghrelin expression in insulinoma (P = 0.014).
Conclusions: Plasma levels of acylated ghrelin decreased in patients with insulinoma, probably due to the hyperinsulinemia and obesity in the patients. Expression of both ghrelin and its receptor is common in insulinoma.
Keywords: BMI; Ghrelin; Growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R); Insulin; Insulinoma; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- R. Arnold, A. Rinke, M. Anlauf, Persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (PHH) in adults: insulinoma and nesidioblastosis. In A Century of Advances in Neuroendocrine Tumor Biology and Treatment, ed. by I.M. Modlin and K. Oberg (Felsenstein, C.C.C.P, Montreaux, 2008), p. 76–85
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

