Community Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Shenzhen, China, 2020
- PMID: 32125269
- PMCID: PMC7258448
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2606.200239
Community Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Shenzhen, China, 2020
Abstract
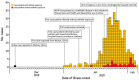
Since early January 2020, after the outbreak of coronavirus infection in Wuhan, China, ≈365 confirmed cases have been reported in Shenzhen, China. The mode of community and intrafamily transmission is threatening residents in Shenzhen. Strategies to strengthen prevention and interruption of these transmissions should be urgently addressed.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus; COVID-19; China; SARS-CoV-2; Shenzhen; community transmission; coronavirus; epidemiologic; respiratory infections; severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses.
Figures
References
-
- Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. NEJM. 2020. Jan 31 [cited 2020 Feb 7]. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

