Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools
- PMID: 32125642
- PMCID: PMC7090474
- DOI: 10.1007/s12250-020-00207-4
Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools
Abstract
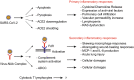
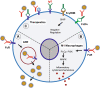
Currently there is no effective antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection, which frequently leads to fatal inflammatory responses and acute lung injury. Here, we discuss the various mechanisms of SARS-CoV-mediated inflammation. We also assume that SARS-CoV-2 likely shares similar inflammatory responses. Potential therapeutic tools to reduce SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory responses include various methods to block FcR activation. In the absence of a proven clinical FcR blocker, the use of intravenous immunoglobulin to block FcR activation may be a viable option for the urgent treatment of pulmonary inflammation to prevent severe lung injury. Such treatment may also be combined with systemic anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. However, these strategies, as proposed here, remain to be clinically tested for effectiveness.
Keywords: Antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE); Fc receptors (FcR); Inflammatory response; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bolles M, Deming D, Long K, Agnihothram S, Whitmore A, Ferris M, Funkhouser W, Gralinski L, Totura A, Heise M, Baric RS. A double-inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus vaccine provides incomplete protection in mice and induces increased eosinophilic proinflammatory pulmonary response upon challenge. J Virol. 2011;85:12201–12215. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06048-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Xia J, Yu T, Zhang X, Zhang L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clay C, Donart N, Fomukong N, Knight JB, Lei W, Price L, Hahn F, Van Westrienen J, Harrod KS. Primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection limits replication but not lung inflammation upon homologous rechallenge. J Virol. 2012;86:4234–4244. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06791-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

