Role of brain renin angiotensin system in neurodegeneration: An update
- PMID: 32127770
- PMCID: PMC7042626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.01.026
Role of brain renin angiotensin system in neurodegeneration: An update
Abstract
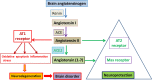
Renin angiotensin system (RAS) is an endocrine system widely known for its physiological roles in electrolyte homeostasis, body fluid volume regulation and cardiovascular control in peripheral circulation. However, brain RAS is an independent form of RAS expressed locally in the brain, which is known to be involved in brain functions and disorders. There is strong evidence for a major involvement of excessive brain angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)/Angiotensin II (Ang II)/Angiotensin type-1 receptor (AT-1R) axis in increased activation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and neuroinflammation causing neurodegeneration in several brain disorders. Numerous studies have demonstrated strong neuroprotective effects by blocking AT1R in these brain disorders. Additionally, the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)/Angiotensin (1-7)/Mas receptor (MASR), is another axis of brain RAS which counteracts the damaging effects of ACE/Ang II/AT1R axis on neurons in the brain. Thus, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) and activation of ACE2/Angiotensin (1-7)/MASR axis may serve as an exciting and novel method for neuroprotection in several neurodegenerative diseases. Here in this review article, we discuss the expression of RAS in the brain and highlight how altered RAS level may cause neurodegeneration. Understanding the pathophysiology of RAS and their links to neurodegeneration has enormous potential to identify potentially effective pharmacological tools to treat neurodegenerative diseases in the brain.
Keywords: Angiotensin; Brain; Neurodegeneration; Neuroprotection; RAS.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad S. Angiotensin receptor antagonists delay nitric oxide-deficient stroke in stroke-prone rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997;333(1):39–45. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed H.A., Ishrat T., Pillai B., Bunting K.M., Patel A., Vazdarjanova A., Waller J.L., Arbab A.S., Ergul A., Fagan S.C. Role of angiotensin system modulation on progression of cognitive impairment and brain MRI changes in aged hypertensive animals – A randomized double- blind pre-clinical study. Behav. Brain Res. 2018;346:29–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amin F.U., Shah S.A., Kim M.O. Glycine inhibits ethanol-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptotic neurodegeneration in postnatal rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2016;96:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Auladell C., de Lemos L., Verdaguer E., Ettcheto M., Busquets O., Lazarowski A., Beas-Zarate C., Olloquequi J., Folch J., Camins A. Role of JNK isoforms in the kainic acid experimental model of epilepsy and neurodegeneration. Front Biosci. 2017;22(5):795–814. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous