Protective Effect and Mechanism of Action of Rosmarinic Acid on Radiation-Induced Parotid Gland Injury in Rats
- PMID: 32127788
- PMCID: PMC7036515
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325820907782
Protective Effect and Mechanism of Action of Rosmarinic Acid on Radiation-Induced Parotid Gland Injury in Rats
Abstract
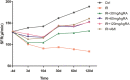
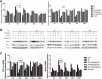
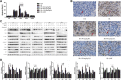
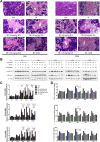
The parotid glands are damaged by oxidative stress and a series of pathophysiological changes after irradiation. Rosmarinic acid (RA) is a natural antioxidant that provides a radioprotective effect against harmful damage from ionizing radiation. The present study aims to explore the protective effects of RA on radiation-induced parotid gland injury and its underlying mechanism. Sprague-Dawley rats were irradiated with 15 Gy X-ray and treated with different concentrations of RA (30, 60, and 120 mg/kg) or amifostine (AMI, 250 mg/kg). Saliva secretion function, oxidative stress, apoptosis, the inflammatory response, and fibrosis were determined by the measurement of the salivary flow rate, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, transferase-mediated DUTP Nick end labeling, Western blot, quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction, and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Here, we show that RA treatment significantly attenuated reactive oxygen species by a direct hindrance effect and the indirect activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 signaling. Rosmarinic acid not only reduced apoptosis by inhibiting p53/jun N-terminal kinase activation but also reduced parotid gland tissue fibrosis by downregulating inflammatory factor levels. Compared to AMI, RA has the obvious advantages of late efficacy and convenient usage. Moreover, 60 mg/kg is the minimum effective dose of RA. Therefore, RA can potentially be applied as a therapeutic radioprotective agent to treat radiation-induced parotid gland injury in the future.
Keywords: apoptosis; fibrosis; oxidative stress; parotid gland; radiation injury; rosmarinic acid.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NADPH oxidase alleviates germ cell apoptosis and ER stress during testicular ischemia reperfusion injury.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Aug;27(8):2174-2184. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.04.024. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32714044 Free PMC article.
-
Injury in Minipig Parotid Glands following Fractionated Exposure to 30 Gy of Ionizing Radiation.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014 Jul;151(1):100-6. doi: 10.1177/0194599814528103. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014. PMID: 24675789
-
Novel protection strategy against X-ray-induced damage to salivary glands.Radiat Res. 1998 Mar;149(3):271-6. Radiat Res. 1998. PMID: 9496890
-
Comparison of effects of dexmedetomidine and amifostine against X-ray radiation-induced parotid damage.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2022 May;61(2):241-253. doi: 10.1007/s00411-022-00964-8. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35147734
-
Histological and biochemical evaluation of the effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNps) versus titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) on rat parotid gland.Ultrastruct Pathol. 2023 Jul 4;47(4):339-363. doi: 10.1080/01913123.2023.2205924. Epub 2023 May 3. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37132546
Cited by
-
Multi‑parameter quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in the early assessment of radiation‑induced parotid damage in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma following intensity‑modulated radiotherapy.Oncol Lett. 2024 Feb 28;27(4):180. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14313. eCollection 2024 Apr. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38464343 Free PMC article.
-
Radioprotective effects and mechanism of HL-003 on radiation-induced salivary gland damage in mice.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12581-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589816 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of rosmarinic acid on ethanol-induced gastritis in male rats: antioxidant defense enhancement.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 May 12;16(3):305-314. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.314829. eCollection 2021 Jun. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34221064 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Rosmarinic Acid and the Extracts of Lamiaceae Plants for the Treatment of Fibrosis of Various Organs.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 24;13(2):146. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020146. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosmarinic Acid Alleviates Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Downregulating the tRNA N7-Methylguanosine Modification-Regulated Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition Through the Exosome Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 22;17:5567-5586. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S458794. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39188632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rettig EM, D’Souza G. Epidemiology of head and neck cancer. Surg Oncol Clin. 2015;24(3):379–396. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Hakim SG, Benedek GA, Su YX, et al. Radioprotective effect of lidocaine on function and ultrastructure of salivary glands receiving fractionated radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(4):e623–e630. - PubMed
-
- Jellema AP, Slotman BJ, Doornaert P, Leemans CR, Langendijk JA. Impact of radiation-induced xerostomia on quality of life after primary radiotherapy among patients with head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69(3):751–760. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

