Spinal epidural abscess secondary to gram-negative bacteria: case report and literature review
- PMID: 32128061
- PMCID: PMC7034427
- DOI: 10.1080/20009666.2019.1705009
Spinal epidural abscess secondary to gram-negative bacteria: case report and literature review
Abstract
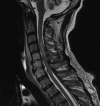
Bacterial spinal epidural abscess (SEA) is a rare suppurative infection that commonly presents with nonspecific symptoms along with the infrequent triad of fever, back pain, and neurological deficits. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, intravenous drug use, degenerative disc disease, infection with human immunodeficiency virus, and recent trauma or surgery. Patients with SEA often experience poor outcomes such as permanent neurological deficits, residual motor weakness, and even death. Staphylococcus aureus is the most predominant organism known to cause SEA; however, gram-negative bacteria are isolated in a small percentage of cases. Here we report three cases of SEA caused by gram-negative organisms. Each patient had identifiable risk factors known to increase the risk for SEA, and upon presentation had symptoms of SEA. Upon work up, the patients had positive cultures for gram-negative organisms and MRI imaging confirmed the presence of SEA. One patient made a full recovery while the other two cases resulted in permanent paraplegia. These cases stress the importance of considering SEA even in the presence of gram-negative infections, despite them being a rare cause. Furthermore, these cases emphasize the importance of broad-spectrum antibiotics that cover gram-negative bacteria in patients found to have risk factors along with symptoms of SEA.
Keywords: Diseases of the nervous system; Gram-negative infection; Spinal epidural abscess.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of Greater Baltimore Medical Center.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Darouiche RO. Spinal epidural abscess. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2012–2020. - PubMed
-
- Gossman W, TL K, Mesfin FB.. Spinal epidural abscess. Updated 2019 July10. In: Baker M, editor. StatPearls. [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441890/
-
- Gellin BG, Weingarten K, Gamache FW, et al. Epidural abscess. In: Scheld WM, Whitley RJ, Durack DT, editors. Infections of the central nervous system. 2nd ed. Philadelphia:Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1997. p. P.507.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
