Sodium valproate ameliorates aluminum-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of PC12 cells
- PMID: 32128102
- PMCID: PMC7038424
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.36930.8804
Sodium valproate ameliorates aluminum-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of PC12 cells
Abstract
Objectives: According to recent studies, valproate shows some protection against oxidative stress (OS) induced by neurotoxins. Current investigation tried to determine the possible ameliorating effects of sodium valproate (SV) against aluminum (Al)-induced cell death, apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and OS in PC12 cells.
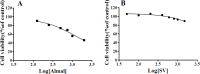
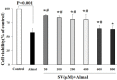
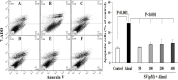
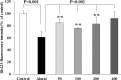
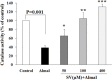
Materials and methods: In this in vitro study, PC12 cells were treated with different concentrations of aluminum maltolate (Almal) with and without SV (50-400 µM). Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. To measure quantitatively the effects of SV on Al-induced apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS), flowcytometry using 7AAD/annexin-V and 2', 7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate staining were employed, respectively. MMP was monitored using the retention of rhodamine 123. Catalase (CAT) activity was assayed by the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
Results: Exposure of PC12 cells for 48 hr to Almal (125-2000 µM) significantly reduced cell viability (IC50=1090 μM), increased ROS generation and apoptosis, and reduced MMP and CAT activity. SV reduced the Almal-induced cell death and apoptosis. Furthermore, the effects of Almal on ROS generation, catalase activity, and MMP reduction were significantly diminished by SV.
Conclusion: Data from this study suggest that SV can inhibit Al-induced cell death and apoptosis of PC12 cells via ameliorating OS.
Keywords: Aluminum maltolate; Apoptosis; Histone deacetylase – inhibitor; Oxidative stress; Valproic acid.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Hydroalcoholic Extract of Saffron Protects PC12 Cells against Aluminum-Induced Cell Death and Oxidative Stress in Vitro.Iran J Med Sci. 2020 Jan;45(1):59-66. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2019.44971. Iran J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32038060 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of nimodipine and lithium against aluminum-induced cell death and oxidative stress in PC12 cells.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Nov;19(11):1251-1257. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27917283 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor protects against aluminum-mediated cell death.Toxicology. 2002 Jul 15;176(3):195-207. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(02)00139-7. Toxicology. 2002. PMID: 12093616
-
Neuroprotective role of hyperforin on aluminum maltolate-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in PC12 cells and SH-SY5Y cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Feb 1;299:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30481499
-
Alpha synuclein protein is involved in Aluminum-induced cell death and oxidative stress in PC12 cells.Brain Res. 2016 Mar 15;1635:153-60. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.01.037. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26826584
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Metal-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neurological Disorders.Toxics. 2021 Jun 17;9(6):142. doi: 10.3390/toxics9060142. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34204190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental Chemical Exposures and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: a Review of Recent Literature.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2022 Dec;9(4):631-649. doi: 10.1007/s40572-022-00371-7. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2022. PMID: 35902457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Whole Genomic Wide Knockout Screening Identifies Specific Genes Associated With PM2.5-Induced Mineral Absorption in Liver Toxicity.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 7;9:669434. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.669434. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34307318 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Aluminum-Induced Neurotoxicity and Alzheimer's Disease: A Focus on Non-Coding RNAs.Neurochem Res. 2024 Nov;49(11):2988-3005. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04214-9. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 39060769 Review.
-
Emerging Neuroprotective Strategies: Unraveling the Potential of HDAC Inhibitors in Traumatic Brain Injury Management.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(14):2298-2313. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240128002056. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38288835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Farhat SM, Mahboob A, Iqbal G, Ahmed T. Aluminum-induced cholinergic deficits in different brain parts and its implications on sociability and cognitive functions in mouse. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;177:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Kaur A, Gill KD. Disruption of neuronal calcium homeostasis after chronic aluminium toxicity in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96:118–122. - PubMed
-
- Saberzadeh J, Arabsolghar R, Takhshid MA. Alpha synuclein protein is involved in Aluminum-induced cell death and oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 2016;1635:153–160. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto T, Saito H, Ishii K, Takahashi H, Tanabe S, Ogasawara Y. Aluminum inhibits proteolytic degradation of amyloid beta peptide by cathepsin D: a potential link between aluminum accumulation and neuritic plaque deposition. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:6543–6549. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
