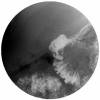
Successful closure of chronic recurrent Enterocutaneous fistula with a concurrent over-the-scope closure and a stent placement
- PMID: 32128164
- PMCID: PMC7044360
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.2652
Successful closure of chronic recurrent Enterocutaneous fistula with a concurrent over-the-scope closure and a stent placement
Abstract
Gastrointestinal ulcers and perforations can occur as a complication of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). Emerging endoscopic technologies can be utilized to successfully intervene perforations that fail surgical intervention. We report a case of perforated duodenal ulcer that failed surgical intervention and, however, was successfully closed with over-the-scope clip (OTSC) closure with concomitant placement of fully covered stent.
Keywords: Enterocutaneous fistula; gastrointestinal perforations; nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs; perforated peptic ulcer; perforations.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Zelickson MS, Bronder CM, Johnson BL, et al. Helicobacter pylori is not the predominant etiology for peptic ulcers requiring operation. Am Surg. 2011;77:1054‐1060. - PubMed
-
- Vasilenko VH, Grebnev AL, Sheptulin AA. Stomach Ulcer. Moscow: Medicine; 1987:288.
-
- Malkov IS, Zaynutdinov AM, Veliyev NA, et al. Laparoscopic and endoscopic management of duodenal ulcers. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198(3):352‐355. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources