Multiple lipid binding sites determine the affinity of PH domains for phosphoinositide-containing membranes
- PMID: 32128410
- PMCID: PMC7030919
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay5736
Multiple lipid binding sites determine the affinity of PH domains for phosphoinositide-containing membranes
Abstract
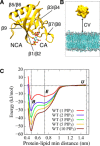
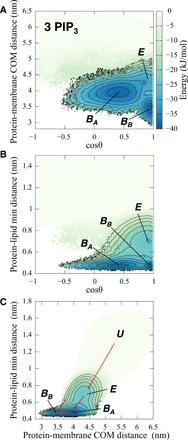
Association of peripheral proteins with lipid bilayers regulates membrane signaling and dynamics. Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains bind to phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) molecules in membranes. The effects of local PIP enrichment on the interaction of PH domains with membranes is unclear. Molecular dynamics simulations allow estimation of the binding energy of GRP1 PH domain to PIP3-containing membranes. The free energy of interaction of the PH domain with more than two PIP3 molecules is comparable to experimental values, suggesting that PH domain binding involves local clustering of PIP molecules within membranes. We describe a mechanism of PH binding proceeding via an encounter state to two bound states which differ in the orientation of the protein relative to the membrane, these orientations depending on the local PIP concentration. These results suggest that nanoscale clustering of PIP molecules can control the strength and orientation of PH domain interaction in a concentration-dependent manner.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interactions of Pleckstrin Homology Domains with Membranes: Adding Back the Bilayer via High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics.Structure. 2016 Aug 2;24(8):1421-1431. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27427480 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and lipid-binding properties of the kindlin-3 pleckstrin homology domain.Biochem J. 2017 Feb 15;474(4):539-556. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160791. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 27974389 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Peripheral Membrane Proteins with Membranes: Free Energy of Binding of GRP1 PH Domain with Phosphatidylinositol Phosphate-Containing Model Bilayers.J Phys Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 7;7(7):1219-24. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00153. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Phys Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26977543 Free PMC article.
-
The energetics of protein-lipid interactions as viewed by molecular simulations.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):25-37. doi: 10.1042/BST20190149. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31872229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational and theoretical approaches for studies of a lipid recognition protein on biological membranes.Biophys Physicobiol. 2017 Oct 26;14:153-160. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.14.0_153. eCollection 2017. Biophys Physicobiol. 2017. PMID: 29159013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Attracted to membranes: lipid-binding domains in plants.Plant Physiol. 2021 Apr 2;185(3):707-723. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaa100. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33793907 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible pivoting of dynamin pleckstrin homology domain catalyzes fission: insights into molecular degrees of freedom.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Jul 1;32(14):1306-1319. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-12-0794. Epub 2021 May 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33979205 Free PMC article.
-
YPIBP: A repository for phosphoinositide-binding proteins in yeast.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jun 24;19:3692-3707. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.06.035. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34285772 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Polyphosphate-Based Compounds as Inhibitors of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Dependent Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 29;21(19):7198. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197198. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33003448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phafins Are More Than Phosphoinositide-Binding Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 30;24(9):8096. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098096. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lemmon M. A., Membrane recognition by phospholipid-binding domains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 99–111 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Carpten J. D., Faber A. L., Horn C., Donoho G. P., Briggs S. L., Robbins C. M., Hostetter G., Boguslawski S., Moses T. Y., Savage S., Uhlik M., Lin A., du J., Qian Y. W., Zeckner D. J., Tucker-Kellogg G., Touchman J., Patel K., Mousses S., Bittner M., Schevitz R., Lai M. H. T., Blanchard K. L., Thomas J. E., A transforming mutation in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1 in cancer. Nature 448, 439–444 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Baraldi E., Carugo K. D., Hyvönen M., Surdo P. L., Riley A. M., Potter B. V. L., O’Brien R., Ladbury J. E., Saraste M., Structure of the PH domain from Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in complex with inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate. Structure 7, 449–460 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

