Otopathology in CHARGE syndrome
- PMID: 32128443
- PMCID: PMC7042646
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.347
Otopathology in CHARGE syndrome
Abstract
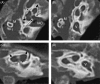
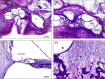
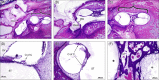
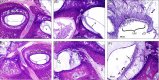
Postmortem temporal bone computed tomography (CT) and histopathologic findings in an infant with CHARGE syndrome revealed bilateral cochleovestibular hypoplasia, including cochlear pathology relevant to cochlear implant candidacy. Both ears had absence of the superior semicircular canals (SCCs), severely hypoplastic posterior SCCs, and hypoplastic (right ear) or absent (left ear) lateral SCCs seen on CT and histopathology. Histopathology further revealed the absence of all SCC ampullae except the right lateral SCC ampulla and atrophic vestibular neuroepithelium in the saccule and utricle bilaterally. The right cochlea consisted of a basal turn with patent round window, and malformed middle turn (type IV cochlear hypoplasia), with a small internal auditory canal (IAC) but near normal cochlear nerve aperture (fossette). Quantification of spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) on histologic sections revealed a reduced SGN population (35% of normal for age), but this ear would still have likely achieved benefit from a cochlear implant based on this population. The left cochlea consisted of only a basal turn with patent round window (type III cochlear hypoplasia) with a small IAC and very small cochlear nerve aperture. Notably, histology revealed that there were no SGNs in the cochlea, and therefore, this ear would not have been a good candidate for cochlear implantation.
Level of evidence: IV.
Keywords: CHARGE syndrome; cochlear implantation; congenital anomalies; otopathology; temporal bone pathology.
© 2020 The Authors. Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Triological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Merchant S, Nadol J. Methods of removal, preparation and study Schuknecht's Pathology of the Ear. Shelton, CT: People's Medical Pub. House‐USA Inc; 2010:3Y51.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
