Efficacy evaluation of personalized coaptation in neurotization for motor deficit after peripheral nerve injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32129004
- PMCID: PMC7177589
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1582
Efficacy evaluation of personalized coaptation in neurotization for motor deficit after peripheral nerve injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Peripheral neurotization, recently as a promising approach, has taken effect in recovering motor function after damage to a peripheral nerve root. Neural anastomosis comprised of nerve conduit and neurorrhaphy participates in the nerve reconstruction. Current literature lacks evidence supporting an individualized coaptation for rescue of locomotor loss in rat subjects with paraplegia secondary to peripheral nerve injury (PNI).
Methods: This meta-analysis intends to qualify the specificity of gap-specific coaptation in treating a paralyzed limb following PNI. We used a highly sensitive search strategy to identify all published studies in multiple databases up to 1 May 2019. All identified trials were systematically evaluated using specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. Cochrane methodology was also applied to the results of this study.
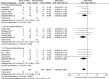
Results: Twelve studies, including 349 rat subjects, met eligibility criteria. For a medium nerve defect (0.5-3.0 cm), nerve conduit was more likely than neurorrhaphy to precipitate axon regeneration and improve motor outcome of the hemiplegic limb (OR = 3.61, 95% CI = 1.80, 7.26, p < .0003) at 3-month follow-up, whereas neurorrhaphy might take its place in promoting limb motor function in a small nerve gap (<0.5 cm) (OR = 0.48, 95% CI = 0.22, 1.07, p < .007). For a small nerve defect, nerve conduit still demonstrated visible effectiveness in recovery of limb motion albeit poorer than neurorrhaphy (OR = 1.50, 95% CI = 0.92, 2.47, p < .05).
Conclusion: Selective neurotization facilitates motor regeneration after nerve transection, and advisable choice of neural coaptation can maximize functional outcome on an individual basis.
Keywords: functional recovery; neurotization; neurotube; peripheral nerve injury; personalized coaptation.
© 2020 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- D'Arpa, S. , Zabbia, G. , Cannizzaro, C. , Salimbeni, G. , Plescia, F. , Mariolo, A. V. , … Cordova, A. (2018). Seeding nerve sutures with minced nerve‐graft (MINE‐G): A simple method to improve nerve regeneration in rats. Acta Chirurgica Belgica, 118(1), 27–35. 10.1080/00015458.2017.1353237 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frank, K. , Englbrecht, M. , Koban, K. C. , Cotofana, S. C. , Stewart, J. K. , Giunta, R. E. , & Schenck, T. L. (2018). Nerve transfer of the anterior interosseous nerve to the thenar branch of the median nerve ‐ An anatomical and histological analysis. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery, 72(5), 751–758. 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.12.017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 81171147/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- ZDRCA2016010/Research Foundation of Health Department of Jiangsu Province/International
- RC201156/Key Personal Medical Research Foundation of Health Department of Jiangsu province/International
- XK201117/Jiangsu province's Key Discipline of Medicine/International
- Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

