The Economic Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Systematic Review
- PMID: 32130134
- PMCID: PMC7059082
- DOI: 10.2196/16866
The Economic Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Positive economic impact is a key decision factor in making the case for or against investing in an artificial intelligence (AI) solution in the health care industry. It is most relevant for the care provider and insurer as well as for the pharmaceutical and medical technology sectors. Although the broad economic impact of digital health solutions in general has been assessed many times in literature and the benefit for patients and society has also been analyzed, the specific economic impact of AI in health care has been addressed only sporadically.
Objective: This study aimed to systematically review and summarize the cost-effectiveness studies dedicated to AI in health care and to assess whether they meet the established quality criteria.
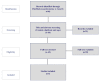
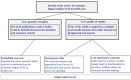
Methods: In a first step, the quality criteria for economic impact studies were defined based on the established and adapted criteria schemes for cost impact assessments. In a second step, a systematic literature review based on qualitative and quantitative inclusion and exclusion criteria was conducted to identify relevant publications for an in-depth analysis of the economic impact assessment. In a final step, the quality of the identified economic impact studies was evaluated based on the defined quality criteria for cost-effectiveness studies.
Results: Very few publications have thoroughly addressed the economic impact assessment, and the economic assessment quality of the reviewed publications on AI shows severe methodological deficits. Only 6 out of 66 publications could be included in the second step of the analysis based on the inclusion criteria. Out of these 6 studies, none comprised a methodologically complete cost impact analysis. There are two areas for improvement in future studies. First, the initial investment and operational costs for the AI infrastructure and service need to be included. Second, alternatives to achieve similar impact must be evaluated to provide a comprehensive comparison.
Conclusions: This systematic literature analysis proved that the existing impact assessments show methodological deficits and that upcoming evaluations require more comprehensive economic analyses to enable economic decisions for or against implementing AI technology in health care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cost-benefit analysis; machine learning; telemedicine.
©Justus Wolff, Josch Pauling, Andreas Keck, Jan Baumbach. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 20.02.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Phelps CE. Health Economics. Abingdon, Oxfordshire: Routledge; 2017.
-
- Statistisches Bundesamt. [2019-10-03]. Health Expenditure in 2017: +4.7% https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2019/03/PD19_109_23....
-
- Whitten PS, Mair FS, Haycox A, May CR, Williams TL, Hellmich S. Systematic review of cost effectiveness studies of telemedicine interventions. Br Med J. 2002 Jun 15;324(7351):1434–7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7351.1434. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/12065269 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elbert N, van Os-Medendorp H, van Renselaar W, Ekeland A, Hakkaart-van Roijen L, Raat H, Nijsten T, Pasmans S. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of eHealth interventions in somatic diseases: a systematic review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J Med Internet Res. 2014 Apr 16;16(4):e110. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2790. https://www.jmir.org/2014/4/e110/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanyal C, Stolee P, Juzwishin D, Husereau D. Economic evaluations of eHealth technologies: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198112. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198112 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical