The beneficial effects of a water-based aerobic exercise session on the blood lipids of women with dyslipidemia are independent of their training status
- PMID: 32130352
- PMCID: PMC7035592
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e1183
The beneficial effects of a water-based aerobic exercise session on the blood lipids of women with dyslipidemia are independent of their training status
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the acute effects of a session of water-based aerobic exercise on the blood lipid levels of women with dyslipidemia and to compare these results according to their training status.
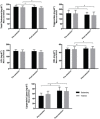
Method: Fourteen premenopausal women with dyslipidemia, aged 40-50 years, participated in two water-based aerobic exercise sessions, the first when they were generally sedentary and the second after they were trained with a water-based aerobic training program for 12 weeks. Both experimental sessions were performed using the same protocol, lasted 45 min, and incorporated an interval method, alternating 3 min at a rating of perceived exertion (RPE) of 13 and 2 min at an RPE of 9. Total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and lipoprotein lipase enzyme (LPL) were obtained through venous blood collection before and immediately after each session. A generalized estimating equation method and Bonferroni tests were conducted (with time and training status as factors) for statistical analyses.
Results: At enrollment, the mean age of the participants was 46.57 years (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.81-48.34). The statistical analyses showed a significant time effect for all variables (TC: p=0.008; TG: p=0.012; HDL: p<0.001; LPL: p<0.001) except for LDL (p=0.307). However, the training status effect was not significant for any variable (TC: p=0.527; TG: p=0.899; HDL: p=0.938; LDL: p=0.522; LPL: p=0.737). These results indicate that the TC and TG levels reduced and the HDL and LPL concentrations increased from pre- to post-session in similar magnitudes in both sedentary and trained women.
Conclusions: A single water-based aerobic exercise session is sufficient and effective to beneficially modify the lipid profile of women with dyslipidemia, regardless of their training status.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr Pract. 2017;23((Suppl 2)):1–87. doi: 10.4158/EP171764.APPGL. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

