Exercise prescription for people with mental illness: an evaluation of mental health professionals' knowledge, beliefs, barriers, and behaviors
- PMID: 32130402
- PMCID: PMC7236166
- DOI: 10.1590/1516-4446-2019-0547
Exercise prescription for people with mental illness: an evaluation of mental health professionals' knowledge, beliefs, barriers, and behaviors
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to understand the knowledge, beliefs, barriers, and behaviors of mental health professionals about physical activity and exercise for people with mental illness.
Methods: The Portuguese version of The Exercise in Mental Illness Questionnaire was used to assess knowledge, beliefs, barriers, and behaviors about exercise prescription for people with mental illness in a sample of 73 mental health professionals (68.5% women, mean age = 37.0 years) from 10 Psychosocial Care Units (Centros de Atenção Psicossocial) in Porto Alegre and Canoas, state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
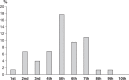
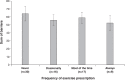
Results: Most of respondents had received no formal training in exercise prescription. Exercise ranked fifth as the most important treatment, and most of the sample never or occasionally prescribed exercise. The most frequently reported barriers were lack of training in physical activity and exercise prescription and social stigma related to mental illness. Professionals who themselves met recommended physical activity levels found fewer barriers to prescribing physical activity and did so with greater frequency.
Conclusion: Exercise is underrated and underused as a treatment. It is necessary to include physical activity and exercise training in mental health curricula. Physically active professionals are more likely to prescribe exercise and are less likely to encounter barriers to doing so. Interventions to increase physical activity levels among mental health professionals are necessary to decrease barriers to and increase the prescription of physical activity and exercise for mental health patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A 10-hours workshop improves physical activity prescription for mental illness knowledge and confidence in health care professionals: a nation-wide multicentre study from Uganda.Disabil Rehabil. 2023 Jan;45(1):170-175. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2021.2003448. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Disabil Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 34779314
-
Do Mental Health Professionals Promote a Healthy Lifestyle among Individuals Experiencing Serious Mental Illness?Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2020 Jun;41(6):531-539. doi: 10.1080/01612840.2019.1688436. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Issues Ment Health Nurs. 2020. PMID: 32286095
-
Barriers to exercise prescription and participation in people with mental illness: the perspectives of nurses working in mental health.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2015 Aug;22(6):440-8. doi: 10.1111/jpm.12205. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2015. PMID: 25855247
-
Public and Healthcare Professionals' Knowledge and Attitudes toward Binge Eating Disorder: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2017 Nov 21;9(11):1267. doi: 10.3390/nu9111267. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29160843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Instruments to assess mental health-related stigma among health professionals and students in health sciences: A systematic psychometric review.J Adv Nurs. 2019 Sep;75(9):1838-1853. doi: 10.1111/jan.13960. Epub 2019 Mar 3. J Adv Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30697780
Cited by
-
The acceptability of lifestyle medicine for the treatment of mental illness: perspectives of people with and without lived experience of mental illness.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 13;24(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17683-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38218774 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Depression and Anxiety: Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2025 Jun;34(3):e70054. doi: 10.1111/inm.70054. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40432290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bidirectional causal relational between frailty and mental illness: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 7;15:1397813. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1397813. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38911707 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity, exercise, and mental disorders: it is time to move on.Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2021 Jul-Sep;43(3):177-184. doi: 10.47626/2237-6089-2021-0237. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2021. PMID: 33890431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
South African mental healthcare providers' views about exercise for people with mental illness.S Afr J Psychiatr. 2024 Apr 30;30:2227. doi: 10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v30i0.2227. eCollection 2024. S Afr J Psychiatr. 2024. PMID: 38726326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, Baxter AJ, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE, et al. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (London, England). 2013;382(9904):1575–1586. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous