Once versus twice daily antihypertensive medications for the control of nocturnal blood pressure: a comparative study
- PMID: 32130547
- PMCID: PMC7056751
- DOI: 10.1186/s43044-020-00045-5
Once versus twice daily antihypertensive medications for the control of nocturnal blood pressure: a comparative study
Abstract
Background: Blood pressure (BP) shows short-term variability within the 24 h, which can only be assessed with 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). It is of utmost importance to control BP throughout the night to reduce incidence of hypertension complications. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of timing and frequency of antihypertensive medications on the average nighttime and 24-h blood pressure control.
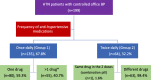
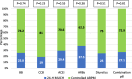
Results: The study enrolled 199 hypertensive patients with controlled office blood pressure; 135 (67.8%) patients were on once daily antihypertensive medication (group 1) while 64 (32.2%) patients were on twice daily doses (group 2). The mean office SBP was 128.7 ± 7.8 mmHg in group 1 vs 129.6 ± 6.6 mmHg in group 2, (p = 0.421). ABPM readings for both groups were as follows: mean daytime SBP was 125.4 ± 11.6 mmHg vs 130.1 ± 12.9, p = 0.011; mean nighttime SBP was 117.0 ± 12.4 mmHg vs 123.1 ± 13.9 mmHg, p = 0.002, and mean 24-h SBP was 122.7 ± 10.6 mmHg vs 127.5 ± 12.0, p = 0.005. The prevalence of non-dipping was 68.9% in group 1 vs 70.3% in group 2 patients, p = 0.8 (the mean dipping ratio was 0.93 ± 0.08 in group 1 vs 0.95 ± 0.07 in group 2, p = 0.198). The prevalence of masked hypertension was higher in group 2 (28.1% vs 43.8%, p = 0.029).
Conclusion: Taking an extra antihypertensive pill at night did not show a decrease in the nighttime or the average 24H blood pressure in hypertensive patients with controlled office BP. On the contrary, patients who used twice daily antihypertensive medications seem to have higher nighttime and 24-h SBP, although the dipping ratio was comparable in both groups.
Keywords: ABPM; Antihypertensive drugs; BP variability; Dipping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of combination olmesartan medoxomil plus azelnidipine versus monotherapy with either agent on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure and pulse rate in Japanese patients with essential hypertension: additional results from the REZALT study.Clin Ther. 2010 May;32(5):861-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.020. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20685495 Clinical Trial.
-
Circadian pattern of ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive patients with and without type 2 diabetes.Chronobiol Int. 2013 Mar;30(1-2):99-115. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2012.701489. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Chronobiol Int. 2013. PMID: 23098178
-
The fixed-dose combination of losartan/hydrochlorothiazide elicits potent blood pressure lowering during nighttime in obese hypertensive patients.J Clin Med Res. 2014 Feb;6(1):8-16. doi: 10.4021/jocmr1649w. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Clin Med Res. 2014. PMID: 24400025 Free PMC article.
-
Dipping Status, Ambulatory Blood Pressure Control, Cardiovascular Disease, and Kidney Disease Progression: A Multicenter Cohort Study of CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2023 Jan;81(1):15-24.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.04.010. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023. PMID: 35709922
-
Short-term reproducibility of ambulatory blood pressure measurements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 35 observational studies.J Hypertens. 2020 Nov;38(11):2095-2109. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002522. J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32555001 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Masked uncontrolled hypertension among elderly black sub-saharan africans compared to younger adults: a cross-sectional in-hospital study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04150-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39232715 Free PMC article.
-
Batteryless implantable device with built-in mechanical clock for automated and precisely timed drug administration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 19;120(51):e2315824120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315824120. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38096418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poulter NR, Savopoulos C, Anjum A, Apostolopoulou M, Chapman N, Cross M, et al. Randomized crossover trial of the impact of morning or evening dosing of antihypertensive agents on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertension. 2018;72(4):870–873. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Rosei EA, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. [2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH)]. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2018;19(11):3-73. Epub 2018/12/07. Linee guida ESC/ESH 2018 per la diagnosi e il trattamento dell'ipertensione arteriosa. Task Force per la Diagnosi e il Trattamento dell'Ipertensione Arteriosa della Societa Europea di Cardiologia (ESC) e della Societa Europea dell'Ipertensione Arteriosa (ESH). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources