Monoaminergic and Kynurenergic Characterization of Frontotemporal Dementia and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum
- PMID: 32130630
- PMCID: PMC7162843
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-020-03002-5
Monoaminergic and Kynurenergic Characterization of Frontotemporal Dementia and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum
Abstract
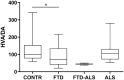
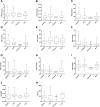
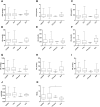
Exploring the neurochemical continuum between frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) with respect to monoamines and kynurenines in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum, may be useful to identify possible new research/therapeutic targets. Hence, we analysed monoamines and kynurenines in CSF and serum derived from patients with FTD (n = 39), ALS (n = 23), FTD-ALS (n = 4) and age-matched control subjects (n = 26), using reversed-phase ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (RP-UHPLC) with electrochemical detection (ECD) and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, respectively. We noted a shared dopaminergic disturbance in FTD and ALS when compared to CONTR, with significantly increased serum DA levels and decreased DOPAC concentrations, as well as decreased DOPAC/DA ratios in both disease groups. In CSF, significantly reduced DOPAC concentrations in FTD and ALS were observed as well. Here, a significant increase in DA levels and decrease in DOPAC/DA ratios was only found in FTD relative to CONTR. With respect to the kynurenine pathway (KP), we only found decreased HK/XA ratios, indicative for vitamin B6 status, in serum of ALS subjects compared to FTD. The dopaminergic commonalities observed in FTD and ALS might relate to a disturbance of dopaminergic nerve terminals in projection areas of the substantia nigra and/or ventral tegmental area, although these findings should first be confirmed in brain tissue. Lastly, based on the results of this work, the KP does not hold promise as a research/therapeutic target in FTD and ALS.
Keywords: Biomarker; Dementia; Neuropathology; Neurophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Majounie E, Renton AE, Mok K, Dopper EG, Waite A, Rollinson S, Chio A, Restagno G, Nicolaou N, Simon-Sanchez J, van Swieten JC, Abramzon Y, Johnson JO, Sendtner M, Pamphlett R, Orrell RW, Mead S, Sidle KC, Houlden H, Rohrer JD, Morrison KE, Pall H, Talbot K, Ansorge O, Chromosome ALSFTDC, French Research Network on FFA, Consortium I. Hernandez DG, Arepalli S, Sabatelli M, Mora G, Corbo M, Giannini F, Calvo A, Englund E, Borghero G, Floris GL, Remes AM, Laaksovirta H, McCluskey L, Trojanowski JQ, Van Deerlin VM, Schellenberg GD, Nalls MA, Drory VE, Lu CS, Yeh TH, Ishiura H, Takahashi Y, Tsuji S, Le Ber I, Brice A, Drepper C, Williams N, Kirby J, Shaw P, Hardy J, Tienari PJ, Heutink P, Morris HR, Pickering-Brown S, Traynor BJ. Frequency of the C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(4):323–330. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70043-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Renton AE, Majounie E, Waite A, Simon-Sanchez J, Rollinson S, Gibbs JR, Schymick JC, Laaksovirta H, van Swieten JC, Myllykangas L, Kalimo H, Paetau A, Abramzon Y, Remes AM, Kaganovich A, Scholz SW, Duckworth J, Ding J, Harmer DW, Hernandez DG, Johnson JO, Mok K, Ryten M, Trabzuni D, Guerreiro RJ, Orrell RW, Neal J, Murray A, Pearson J, Jansen IE, Sondervan D, Seelaar H, Blake D, Young K, Halliwell N, Callister JB, Toulson G, Richardson A, Gerhard A, Snowden J, Mann D, Neary D, Nalls MA, Peuralinna T, Jansson L, Isoviita VM, Kaivorinne AL, Holtta-Vuori M, Ikonen E, Sulkava R, Benatar M, Wuu J, Chio A, Restagno G, Borghero G, Sabatelli M, Consortium I. Heckerman D, Rogaeva E, Zinman L, Rothstein JD, Sendtner M, Drepper C, Eichler EE, Alkan C, Abdullaev Z, Pack SD, Dutra A, Pak E, Hardy J, Singleton A, Williams NM, Heutink P, Pickering-Brown S, Morris HR, Tienari PJ, Traynor BJ. A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron. 2011;72(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Langenhove T, van der Zee J, Gijselinck I, Engelborghs S, Vandenberghe R, Vandenbulcke M, De Bleecker J, Sieben A, Versijpt J, Ivanoiu A, Deryck O, Willems C, Dillen L, Philtjens S, Maes G, Baumer V, Van Den Broeck M, Mattheijssens M, Peeters K, Martin JJ, Michotte A, Santens P, De Jonghe P, Cras P, De Deyn PP, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C. Distinct clinical characteristics of C9orf72 expansion carriers compared with GRN, MAPT, and nonmutation carriers in a Flanders-Belgian FTLD cohort. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70(3):365–373. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamaneurol.181. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Oda T. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT, Bruce J, Schuck T, Grossman M, Clark CM, McCluskey LF, Miller BL, Masliah E, Mackenzie IR, Feldman H, Feiden W, Kretzschmar HA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314(5796):130–133. doi: 10.1126/science.1134108. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

