Stochastic Model of T Cell Repolarization during Target Elimination I
- PMID: 32130873
- PMCID: PMC7136350
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.01.045
Stochastic Model of T Cell Repolarization during Target Elimination I
Abstract
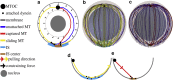
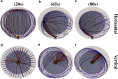
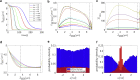
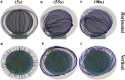
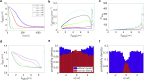
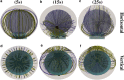
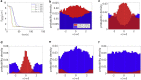
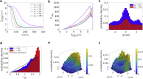
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (T) and natural killer cells are the main cytotoxic killer cells of the human body to eliminate pathogen-infected or tumorigenic cells (i.e., target cells). Once a natural killer or T cell has identified a target cell, they form a tight contact zone, the immunological synapse (IS). One then observes a repolarization of the cell involving the rotation of the microtubule (MT) cytoskeleton and a movement of the MT organizing center (MTOC) to a position that is just underneath the plasma membrane at the center of the IS. Concomitantly, a massive relocation of organelles attached to MTs is observed, including the Golgi apparatus, lytic granules, and mitochondria. Because the mechanism of this relocation is still elusive, we devise a theoretical model for the molecular-motor-driven motion of the MT cytoskeleton confined between plasma membrane and nucleus during T cell polarization. We analyze different scenarios currently discussed in the literature, the cortical sliding and capture-shrinkage mechanisms, and compare quantitative predictions about the spatiotemporal evolution of MTOC position and MT cytoskeleton morphology with experimental observations. The model predicts the experimentally observed biphasic nature of the repositioning due to an interplay between MT cytoskeleton geometry and motor forces and confirms the dominance of the capture-shrinkage over the cortical sliding mechanism when the MTOC and IS are initially diametrically opposed. We also find that the two mechanisms act synergistically, thereby reducing the resources necessary for repositioning. Moreover, it turns out that the localization of dyneins in the peripheral supramolecular activation cluster facilitates their interaction with the MTs. Our model also opens a way to infer details of the dynein distribution from the experimentally observed features of the MT cytoskeleton dynamics. In a subsequent publication, we will address the issue of general initial configurations and situations in which the T cell established two ISs.
Copyright © 2020 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Rudolph M.G., Stanfield R.L., Wilson I.A. How TCRs bind MHCs, peptides, and coreceptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006;24:419–466. - PubMed
-
- Zinkernagel R.M., Doherty P.C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974;248:701–702. - PubMed
-
- Wucherpfennig K.W. T cell receptor crossreactivity as a general property of T cell recognition. Mol. Immunol. 2004;40:1009–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

