Testing of the Survivin Suppressant YM155 in a Large Panel of Drug-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 32131402
- PMCID: PMC7139505
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030577
Testing of the Survivin Suppressant YM155 in a Large Panel of Drug-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cell Lines
Abstract
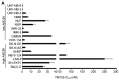
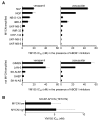
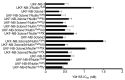
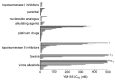
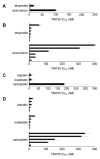
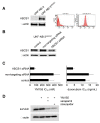
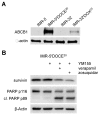
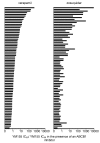
The survivin suppressant YM155 is a drug candidate for neuroblastoma. Here, we tested YM155 in 101 neuroblastoma cell lines (19 parental cell lines, 82 drug-adapted sublines). Seventy seven (77) cell lines displayed YM155 IC50s in the range of clinical YM155 concentrations. ABCB1 was an important determinant of YM155 resistance. The activity of the ABCB1 inhibitor zosuquidar ranged from being similar to that of the structurally different ABCB1 inhibitor verapamil to being 65-fold higher. ABCB1 sequence variations may be responsible for this, suggesting that the design of variant-specific ABCB1 inhibitors may be possible. Further, we showed that ABCC1 confers YM155 resistance. Previously, p53 depletion had resulted in decreased YM155 sensitivity. However, TP53-mutant cells were not generally less sensitive to YM155 than TP53 wild-type cells in this study. Finally, YM155 cross-resistance profiles differed between cells adapted to drugs as similar as cisplatin and carboplatin. In conclusion, the large cell line panel was necessary to reveal an unanticipated complexity of the YM155 response in neuroblastoma cell lines with acquired drug resistance. Novel findings include that ABCC1 mediates YM155 resistance and that YM155 cross-resistance profiles differ between cell lines adapted to drugs as similar as cisplatin and carboplatin.
Keywords: ABCB1; ABCC1; YM155; drug resistance; neuroblastoma; survivin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

