Metabolic Fingerprint of Turner Syndrome
- PMID: 32131408
- PMCID: PMC7141341
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9030664
Metabolic Fingerprint of Turner Syndrome
Abstract
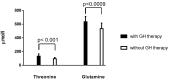
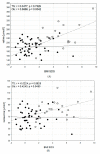
Girls with Turner syndrome (TS) are at increased risk of developing insulin resistance and coronary artery disease as a result of hypertension and obesity frequently seen in these patients. On the other hand, it is known that obesity is associated with increased serum levels of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs: valine; leucine and isoleucine) and aromatic amino acids. The aim of the study is to compare the metabolic fingerprint of girls with TS to the metabolic fingerprint of girls with obesity. Metabolic fingerprinting using an untargeted metabolomic approach was examined in plasma from 46 girls with TS (study group) and 22 age-matched girls with obesity (control group). The mean values of BCAAs, methionine, phenylalanine, lysine, tryptophan, histidine, tyrosine, alanine and ornithine were significantly lower in the study group than in the control (p from 0.0025 to <0.000001). Strong significant correlation between BCAAs, phenylalanine, arginine, tyrosine, glutamic acid, citrulline and alanine, and body mass index expressed as standard deviation score BMI-SDS in the patients with obesity (p from 0.049 to 0.0005) was found. In contrast; there was no correlation between these amino acids and BMI-SDS in the girls with TS. It is suggested that obesity in patients with TS is not associated with altered amino acids metabolism.
Keywords: Turner syndrome; amino acids; branched-chain amino acids; metabolomics; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gravholt C.H., Hjerrild B.E., Mosekilde L., Hansen T.K., Rasmussen L.M., Frystyk J., Flyvbjerg A., Christiansen J.S. Body composition is distinctly altered in Turner syndrome: Relations to glucose metabolism, circulating adipokines, and endothelial adhesion molecules. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006;155:583–592. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.02267. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sagi L., Zuckerman-Levin N., Gawlik A., Ghizzoni L., Buyukgebiz A., Rakover Y., Bistritzer T., Admoni O., Vottero A., Baruch O., et al. Clinical significance of the parental origin of the X chromosome in turner syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;92:846–852. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0158. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

