Continuous renal replacement therapy in elderly with acute kidney injury
- PMID: 32131572
- PMCID: PMC7061002
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2019.431
Continuous renal replacement therapy in elderly with acute kidney injury
Erratum in
-
Continuous renal replacement therapy in elderly with acute kidney injury.Korean J Intern Med. 2020 May;35(3):740. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2019.431.e1. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Korean J Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32392665 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
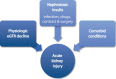
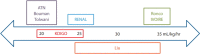
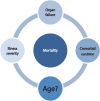
The objective of this article is to raise awareness among physicians of the increasing incidence of acute kidney injury in the elderly population and the utility of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) in its management. While CRRT is frequently applied in younger patients, its use in elderly patients is less frequent, for various reasons, including resistance to such an aggressive intervention from the family and the healthcare team. However, predictors of prognosis have been identified and some studies have concluded that advanced age is not associated with poor outcomes. Decisions regarding management are more complex when dealing with the elderly but like very other patient, the approach should be patient- centered.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Aged; Continuous renal replacement therapy; Critical illness.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
