Lung transplant referral practice patterns: a survey of cystic fibrosis physicians and general pulmonologists
- PMID: 32131782
- PMCID: PMC7055110
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-020-1067-4
Lung transplant referral practice patterns: a survey of cystic fibrosis physicians and general pulmonologists
Abstract
Background: Many individuals with cystic fibrosis (CF) die from respiratory failure without referral for lung transplant. Physician practices that may expedite, delay, or preclude referral, are poorly understood.
Methods: Two parallel, web-based surveys focusing on lung transplant referral triggers and barriers, as well as pre-referral evaluation, were emailed to pulmonologists practicing in the New England region. One questionnaire was sent to CF providers (n = 61), and the second to general pulmonary providers practicing at the same institutions (n = 61).
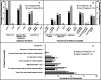
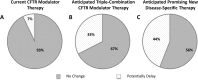
Results: There were 43 (70%) responses to the CF provider survey, and 25 (41%) responses to the general pulmonary ('non-CF') provider survey. Primary reasons for CF providers to refer their patients included: rapidly declining lung function (91%) and a forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) below 30% predicted (74%). The greatest barriers to referral for both CF and non-CF providers included active tobacco use (65 and 96%, respectively, would not refer), and active alcohol or other substance use or dependence (63 and 80%). Furthermore, up to 42% of CF providers would potentially delay their referral if triple-combination therapy or other promising new, disease-specific therapy were anticipated. In general, non-CF providers perform a more robust pre-referral medical work-up, while CF providers complete a psychosocial evaluation in higher numbers. Across both groups, communication with lung transplant programs was reported to be inadequate.
Conclusions: Physician-level barriers to timely lung transplant referral exist and need to be addressed. Enhanced communication between lung transplant programs and pulmonary providers may reduce these barriers.
Keywords: Cystic fibrosis; Lung transplantation; Physician survey; Referral.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
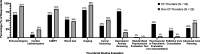

References
-
- Weill D, Benden C, Corris PA, Dark JH, Davis RD, Keshavjee S, Lederer DJ, Mulligan MJ, Patterson GA, Singer LG, Snell GI, Verleden GM, Zamora MR, Glanville AR. A consensus document for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2014 – an update from the pulmonary transplantation council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015;34(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.06.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, Hayes D, Hsich E, Khush KK, Meiser B, Potena L, Rossano JW, Toll AE, Singh TP, Sadavarte A, Zuckermann A, Stehlik J. The international thoracic organ transplant registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-sixth adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2019; focus theme: donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38(10):1042–1055. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2019.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramos KJ, Smith PJ, McKone EF, Pilewski JM, Lucy A, Hempstead SE, Tallarico E, Faro A, Rosenbluth DB, Gray AL, Dunitz JM. Lung transplant referral for individuals with cystic fibrosis: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus guidelines. J Cyst Fibros. 2019;18:321–333. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2019.03.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

