Content and system development of a digital patient-provider communication tool to support shared decision making in chronic health care: InvolveMe
- PMID: 32131808
- PMCID: PMC7057594
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-020-1065-8
Content and system development of a digital patient-provider communication tool to support shared decision making in chronic health care: InvolveMe
Abstract
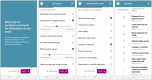
Background: Chronic conditions present major health problems, affecting an increasing number of individuals who experience a variety of symptoms that impact their health related quality of life. Digital tools can be of support in chronic conditions, potentially improving patient-provider communication, promoting shared decision making for treatment and care, and possibly even improving patient outcomes. This study aimed to develop a digital tool for patient-provider communication in chronic health care settings and describes the data collection and subsequent content and software development of the InvolveMe tool. InvolveMe will provide patients with the opportunity to report symptoms and preferences to their health care providers (HCP), and to use secure messaging to interact with the HCPs.
Method: The study employed a combination of interviews with patients with chronic conditions and focus groups with HCPs, examining experiences with chronic conditions and the potential use of a digital tool for support. Participants were recruited from two outpatient clinics at a university hospital. Data collected from interviews and focus groups were analysed using thematic analysis. Content and software development was informed by the data collection and by tool development workshops.
Results: Analyses from interviews with patients (n = 14) and focus groups with HCPs (n = 11) generated three main themes: 1) Making symptoms and challenges visible, 2) Mastering a new life, and 3) Digital opportunities for follow-up. Each main theme generated separate subthemes. Theme 1 and 2 gave input for content development of the symptom and needs assessment part of the tool, while theme 3 provided ideas for the software development of the InvolveMe tool. Tool development workshops with patients (n = 6) and HCPs (n = 6) supplemented the development.
Conclusions: A digital tool such as InvolveMe has the potential to support shared decision making for patients with chronic health conditions. Through integration with an existing patient portal such a tool can provide opportunities for meaningful interactions and communication between patients and HCP's, particularly with regards to symptoms, needs and preferences for care.
Keywords: Digital assessment; Digital communication; Non-functioning pituitary adenoma; Patient centered care; Patient-provider communication; Patient-provider interaction; Renal transplant recipients; Secure messaging; Shared decision making; eHealth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Digital Patient-Provider Communication Intervention (InvolveMe): Qualitative Study on the Implementation Preparation Based on Identified Facilitators and Barriers.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Apr 8;23(4):e22399. doi: 10.2196/22399. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33830063 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of a Digital Patient-Provider Communication Intervention to Support Shared Decision-Making in Chronic Health Care, InvolveMe: Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Apr 7;6(4):e34738. doi: 10.2196/34738. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35389356 Free PMC article.
-
eHealth Technologies, Multimorbidity, and the Office Visit: Qualitative Interview Study on the Perspectives of Physicians and Nurses.J Med Internet Res. 2018 Jan 26;20(1):e31. doi: 10.2196/jmir.8983. J Med Internet Res. 2018. PMID: 29374004 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Age Transformation in Patient-Physician Communication: 25-Year Narrative Review (1999-2023).J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 16;27:e60512. doi: 10.2196/60512. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39819592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Same goals, different challenges: A systematic review of perspectives of people with diabetes and healthcare professionals on Type 2 diabetes care.Diabet Med. 2021 Sep;38(9):e14625. doi: 10.1111/dme.14625. Epub 2021 Jul 11. Diabet Med. 2021. PMID: 34154035
Cited by
-
Development of a Digital Tool for People With a Long-Term Condition Using Stroke as a Case Example: Participatory Design Approach.JMIR Hum Factors. 2022 Jun 3;9(2):e35478. doi: 10.2196/35478. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022. PMID: 35657650 Free PMC article.
-
A Digital Patient-Provider Communication Intervention (InvolveMe): Qualitative Study on the Implementation Preparation Based on Identified Facilitators and Barriers.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Apr 8;23(4):e22399. doi: 10.2196/22399. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33830063 Free PMC article.
-
Usability Testing of a Mobile Health Application for Self-Management of Serious Mental Illness in a Norwegian Community Mental Health Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 17;18(16):8667. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168667. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34444416 Free PMC article.
-
Looking beyond the eyes of the patient: The importance of effective communication in the treatment of age-related macular degeneration.Acta Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar;103(2):205-214. doi: 10.1111/aos.16777. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Acta Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39450444 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of a Digital Patient-Provider Communication Intervention to Support Shared Decision-Making in Chronic Health Care, InvolveMe: Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Apr 7;6(4):e34738. doi: 10.2196/34738. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35389356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- May CR, Cummings A, Myall M, Harvey J, Pope C, Griffiths P, et al. Experiences of long-term life-limiting conditions among patients and carers: what can we learn from a meta-review of systematic reviews of qualitative studies of chronic heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic kidney disease? BMJ Open. 2016;6(10):e011694. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011694. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous