Implementation of a gait center training to improve walking ability and vital parameters in inpatient neurological rehabilitation- a cohort study
- PMID: 32131857
- PMCID: PMC7055071
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-020-00669-3
Implementation of a gait center training to improve walking ability and vital parameters in inpatient neurological rehabilitation- a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Many studies showed that robot-assisted gait training might improve walking of patients after stroke. The question remains whether patients with other neurological diagnoses can improve their ability to walk by training in a gait center. Aim of the present study was therefore to investigate the effects of a gait center training in inpatient neurological rehabilitation on walking ability.
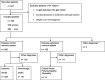
Methods: We implemented a gait center training in addition to individual inpatient rehabilitation. Our primary outcome was walking ability based on the Functional Ambulation Categories (FAC). Our secondary outcomes were vital capacity and blood pressure. We predefined subgroups of patients with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke and critical illness myopathy (CIM) and polyneuropathy (CIP).
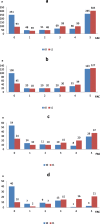
Results: We included 780 patients from our inpatient rehabilitation center in our cohort study. We analyzed 329 patients with ischemic, 131 patients with hemorrhagic stroke and 74 patients with CIP/ CIM. A large number of patients were able to improve their ability to walk. At the end of rehabilitation, patients with ischemic stroke and FAC 3 = increased theirFAC scores by 5%, FAC 4 = 4% and FAC 5 = 7%. Patients with hemorrhagic stroke and FAC 3 = increased by 5%, FAC 4 = 11% and FAC 5 = 9% and patients with CIP/CIM increased by FAC 3 = 3%, FAC 4 = 22% and FAC 5 = 26%. The largest improvement in walking ability during rehabilitation had patients with a FAC = 1 at baseline who improved by a median of 1.4 FAC points (p < 0.001). After adjusting for the number of gait training sessions, the largest improvement in walking ability during rehabilitation had patients with a FAC = 0 at baseline who improved by 1.8 FAC points (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Implementation of an additional gait center training may significantly improve walking ability in neurological rehabilitation.
Keywords: CIP/CIM; Gait center training; Rehabilitation; Stroke; Vital parameter; Walking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Han EY, et al. Robot-assisted gait training improves brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and peak aerobic capacity in subacute stroke patients with totally dependent ambulation: randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95(41):e5078. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005078. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

