The JNK pathway represents a novel target in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through the suppression of MMP-3
- PMID: 32131874
- PMCID: PMC7371465
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01595-9
The JNK pathway represents a novel target in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis through the suppression of MMP-3
Abstract
Background and aim: The pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by excess production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by neutrophils and macrophages in synovium. Additionally, these cytokines promote the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and increased production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), including MMP-3, in synoviocytes that result in joint destruction. There is limited information on how proteolytic enzymes such as MMP-3 can be regulated. We evaluated the effect of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on RA and identified the relationship between the c-Jun N terminal kinase (JNK) pathway and MMP-3. We hypothesized that elucidating this relationship would lead to novel therapeutic approaches to RA treatment and management.
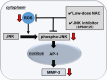
Methods: We investigated the effect of administering a low dose (1000 μM or less) of an antioxidant (NAC) to human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes (MH7A cells). We also investigated the response of antioxidant genes such as nuclear factor erythroid -derived 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Sequestosome 1 (p62). The influence of MMP-3 expression on the JNK pathway leading to joint destruction and the mechanisms underlying this relationship were investigated through primary dispersion culture cells collected from the synovial membranes of RA patients, consisting of rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS).
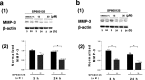
Results: Low-dose NAC (1000 μM) increased the expression of Nrf2 and phospho-p62 in MH7A cells, activating antioxidant genes, suppressing the expression of MMP-3, and inhibiting the phosphorylation of JNK. ROS, MMP-3 expression, and IL-6 was suppressed by administering 30 μM of SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor) in MH7A cells. Furthermore, the administration of SP600125 (30 μM) to RA-FLS suppressed MMP-3.
Conclusions: We demonstrated the existence of an MMP-3 suppression mechanism that utilizes the JNK pathway in RA-FLS. We consider that the JNK pathway could be a target for future RA therapies.
Keywords: JNK pathway; Low-dose NAC; MH7A; MMP-3; RA-FLS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li J, Li J, Yue Y, Hu Y, Cheng W, Liu R, Pan X, Zhang P. Genistein suppresses tumor necrosis factor α-induced inflammation via modulating reactive oxygen species/Akt/nuclear factor κB and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signal pathways in human synoviocyte MH7A cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:315–323. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52354. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

