Initial Glycemic Control and Care Among Younger Adults Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 32132007
- PMCID: PMC7171948
- DOI: 10.2337/dc19-1380
Initial Glycemic Control and Care Among Younger Adults Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing among adults under age 45. Onset of type 2 diabetes at a younger age increases an individual's risk for diabetes-related complications. Given the lasting benefits conferred by early glycemic control, we compared glycemic control and initial care between adults with younger onset (21-44 years) and mid-age onset (45-64 years) of type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: Using data from a large, integrated health care system, we identified 32,137 adults (aged 21-64 years) with incident diabetes (first HbA1c ≥6.5% [≥48 mmol/mol]). We excluded anyone with evidence of prior type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus, or type 1 diabetes. We used generalized linear mixed models, adjusting for demographic and clinical variables, to examine differences in glycemic control and care at 1 year.
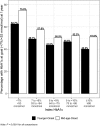
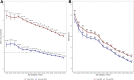
Results: Of identified individuals, 26.4% had younger-onset and 73.6% had mid-age-onset type 2 diabetes. Adults with younger onset had higher initial mean HbA1c values (8.9% [74 mmol/mol]) than adults with onset in mid-age (8.4% [68 mmol/mol]) (P < 0.0001) and lower odds of achieving an HbA1c <7% (<53 mmol/mol) 1 year after the diagnosis (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.70 [95% CI 0.66-0.74]), even after accounting for HbA1c at diagnosis. Adults with younger onset had lower odds of in-person primary care contact (aOR 0.82 [95% CI 0.76-0.89]) than those with onset during mid-age, but they did not differ in telephone contact (1.05 [0.99-1.10]). Adults with younger onset had higher odds of starting metformin (aOR 1.20 [95% CI 1.12-1.29]) but lower odds of adhering to that medication (0.74 [0.69-0.80]).
Conclusions: Adults with onset of type 2 diabetes at a younger age were less likely to achieve glycemic control at 1 year following diagnosis, suggesting the need for tailored care approaches to improve outcomes for this high-risk patient population.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
This article is featured in a podcast available at https://www.diabetesjournals.org/content/diabetes-core-update-podcasts.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention United States Diabetes Surveillance System: diagnosed diabetes [Internet]. Available from https://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/diabetes/DiabetesAtlas.html. Accessed 22 October 2019.
-
- Hillier TA, Pedula KL. Complications in young adults with early-onset type 2 diabetes: losing the relative protection of youth. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2999–3005 - PubMed
-
- Eppens MC, Craig ME, Cusumano J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes complications in adolescents with type 2 compared with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1300–1306 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

