Safety of Liraglutide in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 32132141
- PMCID: PMC7133133
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11881019
Safety of Liraglutide in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide demonstrated cardiovascular and kidney benefits in the LEADER trial, particularly in participants with CKD.
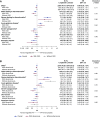
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This post hoc analysis evaluated the safety of liraglutide treatment in patients with CKD in LEADER. Overall, 9340 patients were randomized to liraglutide or placebo, both in addition to standard of care. Of those, 2158 patients had CKD versus 7182 without CKD (defined as eGFR <60 versus ≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2, respectively); 966 patients had macroalbuminuria and 2456 had microalbuminuria (urine albumin-creatinine ratio >300 mg/g and ≥30 to ≤300 mg/g, respectively). At baseline, the mean eGFR in patients with CKD was 46±11 ml/min per 1.73 m2 versus 91±22 ml/min per 1.73 m2 in those without CKD. Time to first event within event groups was analyzed using Cox regression with treatment group, baseline eGFR group, or baseline albuminuria group as fixed factors.
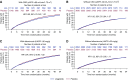
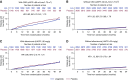
Results: Overall, serious adverse events were more frequently recorded in patients with CKD compared with those without CKD (59% versus 50%; interaction P=0.11); however, they occurred to the same extent in those on liraglutide versus placebo. Similarly, no interaction of adverse events with randomized therapy was observed in patients with micro- or macro- versus normoalbuminuria (interaction P=0.11). Risk of severe hypoglycemia was significantly reduced with liraglutide versus placebo in patients with CKD or with micro- or macroalbuminuria (hazard ratio, 0.63 [95% CI, 0.43 to 0.91] and 0.57 [95% CI, 0.40 to 0.82], respectively).
Conclusions: In LEADER, the use of liraglutide in those with CKD was safe, with no difference between patients with and without CKD.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov; NCT01179048 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01179048).
Keywords: GFR; albumins; chronic kidney disease; chronic renal insufficiency; confidence intervals; creatinine; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; humans; hypoglycemia; kidney; liraglutide; microalbuminuria; standard of care; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Liraglutide for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Safety in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Liraglutide and Diabetic Kidney Disease.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Apr 7;15(4):444-446. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01260120. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32149722 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- De Cosmo S, Viazzi F, Pacilli A, Giorda C, Ceriello A, Gentile S, Russo G, Rossi MC, Nicolucci A, Guida P, Di Bartolo P, Pontremoli R; AMD-Annals Study Group: Achievement of therapeutic targets in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: Insights from the Associazione Medici Diabetologi Annals initiative. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30: 1526–1533, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Papademetriou V, Lovato L, Doumas M, Nylen E, Mottl A, Cohen RM, Applegate WB, Puntakee Z, Yale JF, Cushman WC; ACCORD Study Group: Chronic kidney disease and intensive glycemic control increase cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 87: 649–659, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Keith DS, Nichols GA, Gullion CM, Brown JB, Smith DH: Longitudinal follow-up and outcomes among a population with chronic kidney disease in a large managed care organization. Arch Intern Med 164: 659–663, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

