Two New SGI1-LK Variants Found in Proteus mirabilis and Evolution of the SGI1-HKL Group of Salmonella Genomic Islands
- PMID: 32132162
- PMCID: PMC7056807
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00875-19
Two New SGI1-LK Variants Found in Proteus mirabilis and Evolution of the SGI1-HKL Group of Salmonella Genomic Islands
Erratum in
-
Erratum for de Curraize et al., "Two New SGI1-LK Variants Found in Proteus mirabilis and Evolution of the SGI1-HKL Group of Salmonella Genomic Islands".mSphere. 2020 May 13;5(3):e00435-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00435-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32404517 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
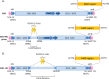
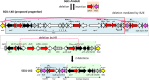
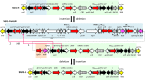
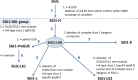
Integrative mobilizable elements belonging to the SGI1-H, -K, and -L Salmonella genomic island 1 (SGI1) variant groups are distinguished by the presence of an alteration in the backbone (IS1359 replaces 2.8 kb of the backbone extending from within traN [S005] to within S009). Members of this SGI1-HKL group have been found in Salmonella enterica serovars and in Proteus mirabilis Two novel variants from this group, designated SGI1-LK1 and SGI1-LK2, were found in the draft genomes of antibiotic-resistant P. mirabilis isolates from two French hospitals. Both variants can be derived from SGI1-PmGUE, a configuration found previously in another P. mirabilis isolate from France. SGI1-LK1 could arise via an IS26-mediated inversion in the complex class 1 integron that duplicated the IS26 element and the target site in IS6100 SGI1-LK1 also has a larger 8.59-kb backbone deletion extending from traN to within S013 and removing traG and traH. However, SGI1-LK1 was mobilized by an IncC plasmid. SGI1-LK2 can be derived from a hypothetical progenitor, SGI1-LK0, that is related to SGI1-PmGUE but lacks the aphA1 gene and one copy of IS26. The integron of SGI1-LK2 could arise via deletion of DNA adjacent to an IS26 and a deletion occurring via homologous recombination between duplicated copies of part of the integron 3'-conserved segment. SGI1-K can also be derived from SGI1-LK0. This would involve an IS26-mediated deletion and an inversion via homologous recombination of a segment between inversely oriented IS26s. Similar events can explain the configuration of the integrons in other SGI1-LK variants.IMPORTANCE Members of the SGI1-HKL subgroup of SGI1-type integrative mobilizable elements have a characteristic alteration in their backbone. They are widely distributed among multiply antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars and Proteus mirabilis isolates. The SGI1-K type, found in the globally disseminated multiply antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky clone ST198 (sequence type 198), and various configurations in the original SGI1-LK group, found in other multiresistant S. enterica serovars and Proteus mirabilis isolates, have complex and highly plastic resistance regions due to the presence of IS26 However, how these complex forms arose and the relationships between them had not been analyzed. Here, a hypothetical progenitor, SGI1-LK0, that can be formed from the simpler SGI1-H is proposed, and the pathways to the formation of new variants, SGI1-LK1 and SGI1-LK2, found in P. mirabilis and other reported configurations via homologous recombination and IS26-mediated events are proposed. This led to a better understanding of the evolution of the SGI1-HKL group.
Keywords: IS26; Proteus mirabilis; SGI1; Salmonella genomic island 1; evolution.
Copyright © 2020 de Curraize et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emergence of Salmonella genomic island 1 (SGI1) among Proteus mirabilis clinical isolates in Dijon, France.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Aug;68(8):1750-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt100. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23580563
-
First report in Africa of two clinical isolates of Proteus mirabilis carrying Salmonella genomic island (SGI1) variants, SGI1-PmABB and SGI1-W.Infect Genet Evol. 2017 Jul;51:132-137. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.03.029. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Infect Genet Evol. 2017. PMID: 28359833
-
A novel variant in Salmonella genomic island 1 of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0399423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03994-23. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38687075 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella genomic islands and antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica.Future Microbiol. 2010 Oct;5(10):1525-38. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.122. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21073312 Review.
-
Genomic islands related to Salmonella genomic island 1; integrative mobilisable elements in trmE mobilised in trans by A/C plasmids.Plasmid. 2021 Mar;114:102565. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2021.102565. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Plasmid. 2021. PMID: 33582118 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of Salmonella Genomic Island 1-Related Elements Among Gamma-Proteobacteria Reveals Their Wide Distribution Among Environmental Species.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 11;13:857492. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.857492. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35479618 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial role of Salmonella genomic island 1 master activator in the parasitism of IncC plasmids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Aug 20;49(14):7807-7824. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab204. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33834206 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic and experimental characterization of SEN1998: a conserved gene carried by the Enterobacteriaceae-associated ROD21-like family of genomic islands.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 14;12(1):2435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06183-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35165310 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of a Highly Pathogenic Proteus Mirabilis Strain Isolated From Dogs in China.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Oct 7;7:589. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00589. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33134334 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing Antibiotic Resistance Caused by Mobile Resistance Genes of High Fitness Cost.mSphere. 2021 Jun 30;6(3):e0035621. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00356-21. Epub 2021 Jun 23. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34160235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siebor E, de Curraize C, Amoureux L, Neuwirth C. 2016. Mobilization of the Salmonella genomic island SGI1 and the Proteus genomic island PGI1 by the A/C2 plasmid carrying blaTEM-24 harboured by various clinical species of Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother 71:2167–2170. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw151. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
