The Bewildering Antitubercular Action of Pyrazinamide
- PMID: 32132245
- PMCID: PMC7062198
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00070-19
The Bewildering Antitubercular Action of Pyrazinamide
Abstract
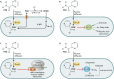
Pyrazinamide (PZA) is a cornerstone antimicrobial drug used exclusively for the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). Due to its ability to shorten drug therapy by 3 months and reduce disease relapse rates, PZA is considered an irreplaceable component of standard first-line short-course therapy for drug-susceptible TB and second-line treatment regimens for multidrug-resistant TB. Despite over 60 years of research on PZA and its crucial role in current and future TB treatment regimens, the mode of action of this unique drug remains unclear. Defining the mode of action for PZA will open new avenues for rational design of novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of TB. In this review, we discuss the four prevailing models for PZA action, recent developments in modulation of PZA susceptibility and resistance, and outlooks for future research and drug development.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; coenzyme A; drug resistance; drug resistance mechanisms; drug susceptibility; mode of action; pyrazinamide; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Boshoff HIM, Xu X, Tahlan K, Dowd CS, Pethe K, Camacho LR, Park T-H, Yun C-S, Schnappinger D, Ehrt S, Williams KJ, Barry CE. 2008. Biosynthesis and recycling of nicotinamide cofactors in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an esssential role for NAD in nonreplicating bacilli. J Biol Chem 283:19329–19341. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800694200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

