Basic Limonoid modulates Chaperone-mediated Proteostasis and dissolve Tau fibrils
- PMID: 32132570
- PMCID: PMC7055235
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-60773-1
Basic Limonoid modulates Chaperone-mediated Proteostasis and dissolve Tau fibrils
Abstract
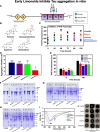
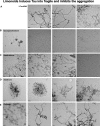
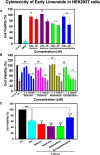
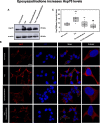
The Alzheimer's disease pathology is associated with accumulation of intracellular neurofibrillary tangles and extracellular senile plaques. The formation of initial nucleus triggers conformational changes in Tau and leads to its deposition. Hence, there is a need to eliminate these toxic proteins for proper functioning of neuronal cells. In this aspect, we screened the effect of basic limonoids such as gedunin, epoxyazadiradione, azadirone and azadiradione on inhibiting Tau aggregation as well as disintegration of induced Tau aggregates. It was observed that these basic limonoids effectively prevented aggregates formation by Tau and also exhibited the property of destabilizing matured Tau aggregates. The molecular docking analysis suggests that the basic limonoids interact with hexapeptide regions of aggregated Tau. Although these limonoids caused the conformational changes in Tau to β-sheet structure, the cytological studies indicate that basic limonoids rescued cell death. The dual role of limonoids in Tau aggregation inhibition and disintegration of matured aggregates suggests them to be potent molecules in overcoming Tau pathology. Further, their origin from a medicinally important plant neem, which known to possess remarkable biological activities was also found to play protective role in HEK293T cells. Basic limonoids were non-toxic to HEK293T cells and also aided in activation of HSF1 by inducing its accumulation in nucleus. Western blotting and immunofluorescence studies showed that HSF1 in downstream increased the transcription of Hsp70 thus, aggravating cytosolic Hsp70 levels that can channel clearance of aberrant Tau. All these results mark basic limonoids as potential therapeutic natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Small molecule-mediated therapeutic approaches to target Tau and Alzheimer's disease.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2025;145:287-304. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2024.11.010. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2025. PMID: 40324850 Review.
-
Tau protein aggregates inhibit the protein-folding and vesicular trafficking arms of the cellular proteostasis network.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 10;294(19):7917-7930. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007527. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30936201 Free PMC article.
-
Neem Derivatives Inhibits Tau Aggregation.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2019 Jun 14;3(1):169-178. doi: 10.3233/ADR-190118. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2019. PMID: 31259310 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein inhibits heparin-induced Tau aggregation by initializing non-toxic Tau oligomer formation.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Feb 12;19(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00704-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33579328 Free PMC article.
-
Limonoids from neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss.) are potential anticancer drug candidates.Med Res Rev. 2024 Mar;44(2):457-496. doi: 10.1002/med.21988. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Med Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37589457 Review.
Cited by
-
HAPLN2 forms aggregates and promotes microglial inflammation during brain aging in mice.PLoS Biol. 2025 Aug 14;23(8):e3003006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003006. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40811716 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial Uptake of Extracellular Tau by Actin-Mediated Phagocytosis.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2761:231-243. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3662-6_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38427240
-
Targeting Chaperone/Co-Chaperone Interactions with Small Molecules: A Novel Approach to Tackle Neurodegenerative Diseases.Cells. 2021 Sep 29;10(10):2596. doi: 10.3390/cells10102596. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-protein coupled receptor, PI3K and Rho signaling pathways regulate the cascades of Tau and amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Biomed. 2021 Jun 10;2(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s43556-021-00036-1. Mol Biomed. 2021. PMID: 35006431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Tau with the chemokine receptor, CX3CR1 and its effect on microglial activation, migration and proliferation.Cell Biosci. 2020 Sep 15;10:109. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00474-4. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32944223 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

