Iron redox pathway revealed in ferritin via electron transfer analysis
- PMID: 32132578
- PMCID: PMC7055317
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-60640-z
Iron redox pathway revealed in ferritin via electron transfer analysis
Abstract
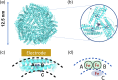
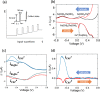
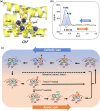
Ferritin protein is involved in biological tissues in the storage and management of iron - an essential micro-nutrient in the majority of living systems. While there are extensive studies on iron-loaded ferritin, its functionality in iron delivery is not completely clear. Here, for the first time, differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) has been successfully adapted to address the challenge of resolving a cascade of fast and co-occurring redox steps in enzymatic systems such as ferritin. Using DPV, comparative analysis of ferritins from two evolutionary-distant organisms has allowed us to propose a stepwise resolution for the complex mix of concurrent redox steps that is inherent to ferritins and to fine-tune the structure-function relationship of each redox step. Indeed, the cyclic conversion between Fe3+ and Fe2+ as well as the different oxidative steps of the various ferroxidase centers already known in ferritins were successfully discriminated, bringing new evidence that both the 3-fold and 4-fold channels can be functional in ferritin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures