Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by INSP3R1-mediated hepatic lipolysis
- PMID: 32132708
- PMCID: PMC7101062
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2074-6
Glucagon stimulates gluconeogenesis by INSP3R1-mediated hepatic lipolysis
Abstract
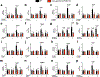
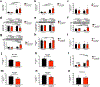
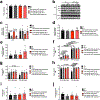
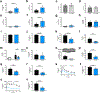
Although it is well-established that reductions in the ratio of insulin to glucagon in the portal vein have a major role in the dysregulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in type-2 diabetes1-3, the mechanisms by which glucagon affects hepatic glucose production and mitochondrial oxidation are poorly understood. Here we show that glucagon stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis by increasing the activity of hepatic adipose triglyceride lipase, intrahepatic lipolysis, hepatic acetyl-CoA content and pyruvate carboxylase flux, while also increasing mitochondrial fat oxidation-all of which are mediated by stimulation of the inositol triphosphate receptor 1 (INSP3R1). In rats and mice, chronic physiological increases in plasma glucagon concentrations increased mitochondrial oxidation of fat in the liver and reversed diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. However, these effects of chronic glucagon treatment-reversing hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance-were abrogated in Insp3r1 (also known as Itpr1)-knockout mice. These results provide insights into glucagon biology and suggest that INSP3R1 may represent a target for therapies that aim to reverse nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type-2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Comment in
-
Glucagon regulates lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation through inositol triphosphate receptor 1 in the liver.J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Jan;12(1):32-34. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13315. Epub 2020 Jul 26. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 32506830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Unger RH Pancreatic glucagon in health and disease. Adv Intern Med 17, 265–288 (1971). - PubMed
Methods-Only References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 DK101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061747/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007324/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114793/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK057751/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA215315/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK118836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023598/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK114954/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA215315/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK116774/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087568/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119968/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045710/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL150234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK112797/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

