Negative Effects of Latent Toxoplasmosis on Mental Health
- PMID: 32132937
- PMCID: PMC7040223
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.01012
Negative Effects of Latent Toxoplasmosis on Mental Health
Abstract
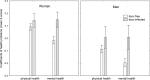
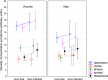
Infection by the parasite Toxoplasma, which affects about 33% of world population, is associated with an increased risk of several mental health disorders, the most strongly with schizophrenia. It is unknown whether schizophrenia is associated with this infection the most strongly, or whether this association has just been the most intensively studied for historical reasons. We used the data from 6,367 subjects tested for toxoplasmosis who took part in an internet survey to search for associations of these infections with 24 mental health disorders and evidence of otherwise impaired mental health. The typical symptom associated with toxoplasmosis was anxiety, and the typical toxoplasmosis-associated disorders were autism (OR = 4.78), schizophrenia (OR = 3.33), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (OR = 2.50), obsessive compulsive disorder (OR = 1.86), antisocial personality disorder (OR = 1.63), learning disabilities (OR = 1.59), and anxiety disorder (OR = 1.48). Toxoplasmosis could play a substantial role in the etiopathogenesis of mental health disorders and its association with schizophrenia is the second strongest association, after autism.
Keywords: Toxoplasma; etiology; infection hypothesis; mental health; prevalence; psychiatric diseases; risk factors.
Copyright © 2020 Flegr and Horáček.
Figures
References
-
- Niebuhr DW, Cowan DN, Millikan AM, Yolken R, Li Y, Weber N. Risk of schizophrenia and antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii among U.S. military personnel. Schizophr Bull (2007) 33:243–4.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

