Southerners Are Wiser Than Northerners Regarding Interpersonal Conflicts in China
- PMID: 32132958
- PMCID: PMC7040192
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00225
Southerners Are Wiser Than Northerners Regarding Interpersonal Conflicts in China
Abstract
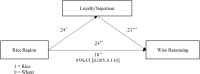
Initial evidence suggests that cultural differences have consequences for wise reasoning (perspective taking, consideration of change and alternatives, intellectual humility, search for compromise, and adopting an outsider's vantage point), with more reports of wise reasoning about interpersonal conflicts among Japanese (as compared to American) young and middle-aged adults. Similarly, we found that people from the rice-farming area of southern China also exhibited greater wise reasoning when they encountered conflicts with a friend or in the workplace than those from the wheat-farming area of northern China (N = 487, 25 provinces). The relationship between rice farming and wise reasoning was mediated by loyalty/nepotism. This research advances study of the relationship between wisdom and culture. It also provides evidence for the influence of social-ecological factors on wisdom and culture.
Keywords: collectivism; conflict; culture; ecology; reasoning; wisdom.
Copyright © 2020 Wei and Wang.
Figures

References
-
- Ardelt M., Pridgen S., Nutter-Pridgen K. L. (2019). “Wisdom as a Personality Type,” in The Cambridge Handbook of Wisdom, Vol. 3 eds Sternberg R. J., Glück J. (Cambridge University Press; ), 144–161. 10.1017/9781108568272.008 - DOI
-
- Basseches M. (1980). Dialectical schemata: a framework for the empirical study of the development of dialectical thinking. Huma. Dev. 23 400–421. 10.1159/000272600 - DOI
-
- Bates D., Mächler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67 133–199. 10.1007/0-387-22747-4_4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

