China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: an updated summary
- PMID: 32133031
- PMCID: PMC7008101
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.01.001
China cardiovascular diseases report 2018: an updated summary
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; Heart failure; Risk factors.
Figures
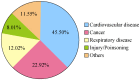
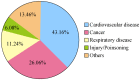
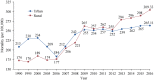
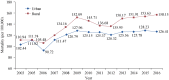
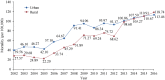
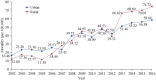
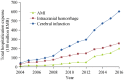
References
-
- Wang Z, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al. Status of hypertension in china: Results from the China hypertension survey, 2012–2015. Circulation. 2018;137:2344–2356. - PubMed
-
- Dong B, Wang HJ, Wang Z, et al. The association of overweight and obesity with blood pressure among Chinese children and adolescents. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013;26:437–444. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Deng Q, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets in Chinese adults: a nationally representative survey of 163,641 adults. Int J Cardiol. 2018;260:196–203. - PubMed
-
- Pan L, Yang Z, Wu Y, et al. The prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Atherosclerosis. 2016;248:2–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
