Deep learning-based single-shot prediction of differential effects of anti-VEGF treatment in patients with diabetic macular edema
- PMID: 32133239
- PMCID: PMC7041458
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.379150
Deep learning-based single-shot prediction of differential effects of anti-VEGF treatment in patients with diabetic macular edema
Abstract
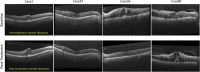
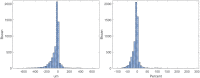
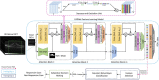
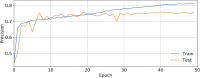
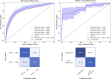
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents are widely regarded as the first line of therapy for diabetic macular edema (DME) but are not universally effective. An automatic method that can predict whether a patient is likely to respond to anti-VEGF therapy can avoid unnecessary trial and error treatment strategies and promote the selection of more effective first-line therapies. The objective of this study is to automatically predict the efficacy of anti-VEGF treatment of DME in individual patients based on optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. We performed a retrospective study of 127 subjects treated for DME with three consecutive injections of anti-VEGF agents. Patients' retinas were imaged using spectral-domain OCT (SD-OCT) before and after anti-VEGF therapy, and the total retinal thicknesses before and after treatment were extracted from OCT B-scans. A novel deep convolutional neural network was designed and evaluated using pre-treatment OCT scans as input and differential retinal thickness as output, with 5-fold cross-validation. The group of patients responsive to anti-VEGF treatment was defined as those with at least a 10% reduction in retinal thickness following treatment. The predictive performance of the system was evaluated by calculating the precision, sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). The algorithm achieved an average AUC of 0.866 in discriminating responsive from non-responsive patients, with an average precision, sensitivity, and specificity of 85.5%, 80.1%, and 85.0%, respectively. Classification precision was significantly higher when differentiating between very responsive and very unresponsive patients. The proposed automatic algorithm accurately predicts the response to anti-VEGF treatment in DME patients based on OCT images. This pilot study is a critical step toward using non-invasive imaging and automated analysis to select the most effective therapy for a patient's specific disease condition.
© 2020 Optical Society of America under the terms of the OSA Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yau J., Rogers S. L., Kawasaki R., Lamoureux E. L., Kowalski J. W., Bek T., Chen S., Dekker J., Fletcher A., Grauslund J., “Meta-Analysis for Eye Disease (METAEYE) Study Group. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy,” Diabetes Care 35(3), 556–564 (2012). 10.2337/dc11-1909 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allingham M. J., Mukherjee D., Lally E. B., Rabbani H., Mettu P. S., Cousins S. W., Farsiu S., “A quantitative approach to predict differential effects of anti-VEGF treatment on diffuse and focal leakage in patients with diabetic macular edema: a pilot study,” Trans. Vis. Sci. Tech. 6(2), 7 (2017). 10.1167/tvst.6.2.7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wells J. A., Glassman A. R., Ayala A. R., Jampol L. M., Bressler N. M., Bressler S. B., Brucker A. J., Ferris F. L., Hampton G. R., Jhaveri C., “Aflibercept, bevacizumab, or ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema: two-year results from a comparative effectiveness randomized clinical trial,” Ophthalmology 123(6), 1351–1359 (2016). 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.02.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
