Turicella otitidis as an Unusual Agent Causing Palmoplantar Eczema: An Emerging Pathogen
- PMID: 32133318
- PMCID: PMC7050971
- DOI: 10.12890/2020_001458
Turicella otitidis as an Unusual Agent Causing Palmoplantar Eczema: An Emerging Pathogen
Abstract
Introduction: Turicella otitidis, described as a new species over 20 years ago, has been isolated mainly from the external ear canal and middle ear fluid. Here, we report the first case of palmoplantar eczema related to T. otitidis.
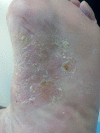
Case presentation: Here, we report the first case of palmoplantar eczema in a 74-year-old female related to T. otitidis.
Conclusions: The question as to whether T. otitidis is a potential pathogen in cases of dyshidrotic eczema is still open, but this could be better elucidated if corynebacteria were speciated more often.
Learning points: The coryneform bacteria Turicella otitidis and Corynebacterium auris were recently detected for the first time in the middle ear of patients with acute otitis media and chronic otitis media.T. otitidis is a potential extraotic pathogen.T. otitidis may be implicated in the pathogenesis of palmoplantar dermatitis.
Keywords: Corynebacteria; Palmoplantar dermatitis; Turicella otitis; eczema.
© EFIM 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interest
Figures
References
-
- Funke G, Stubbs S, Altwegg M, Carlotti A, Collins MD. Turicella otitidis gen. nov., sp. nov., a coryneform bacterium isolated from patients with otitis media. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994;44:270–273. - PubMed
-
- von Graevenitz A, Funke G. Turicella otitidis and Corynebacterium auris: 20 years on. Infection. 2014;42(1):1–4. - PubMed
-
- Jeziorski E, Marchandin H, Jean-Pierre H, Guyon G, Ludwig C, Lalande M, et al. [Turicella otitidis infection: otitis media complicated by mastoiditis]. Arch Pediatr. 2009;16(3):243–247. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources