A Method for Producing Highly Pure Magnetosomes in Large Quantity for Medical Applications Using Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1 Magnetotactic Bacteria Amplified in Minimal Growth Media
- PMID: 32133346
- PMCID: PMC7041420
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00016
A Method for Producing Highly Pure Magnetosomes in Large Quantity for Medical Applications Using Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1 Magnetotactic Bacteria Amplified in Minimal Growth Media
Abstract
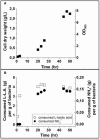
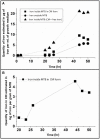
We report the synthesis in large quantity of highly pure magnetosomes for medical applications. For that, magnetosomes are produced by MSR-1 Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense magnetotactic bacteria using minimal growth media devoid of uncharacterized and toxic products prohibited by pharmaceutical regulation, i.e., yeast extract, heavy metals different from iron, and carcinogenic, mutagenic and reprotoxic agents. This method follows two steps, during which bacteria are first pre-amplified without producing magnetosomes and are then fed with an iron source to synthesize magnetosomes, yielding, after 50 h of growth, an equivalent OD565 of ~8 and 10 mg of magnetosomes in iron per liter of growth media. Compared with magnetosomes produced in non-minimal growth media, those particles have lower concentrations in metals other than iron. Very significant reduction or disappearance in magnetosome composition of zinc, manganese, barium, and aluminum are observed. This new synthesis method paves the way towards the production of magnetosomes for medical applications.
Keywords: iron incorporation; magnetosome; magnetotactic bacteria; metals; minimal medium; yeast extract.
Copyright © 2020 Berny, Le Fèvre, Guyot, Blondeau, Guizonne, Rousseau, Bayan and Alphandéry.
Figures


References
-
- Alphandéry E., Idbaih A., Adam C., Delattre J.-Y., Schmitt C., Guyot F., et al. (2017). Development of non-pyrogenic magnetosome minerals coated with poly-l-lysine leading to full disappearance of intracranial U87-Luc glioblastoma in 100% of treated mice using magnetic hyperthermia. Biomaterials 141, 210–222. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.06.026 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amor M., Busigny V., Louvat P., Tharaud M., Gélabert A., Cartigny P., et al. (2018). Iron uptake and magnetite biomineralization in the magnetotactic bacterium Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1: an iron isotope study. Geochim Cosmochim. Acta 232, 225–243. 10.1016/j.gca.2018.04.020 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

