Artificial intelligence in oncology
- PMID: 32133724
- PMCID: PMC7226189
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14377
Artificial intelligence in oncology
Abstract
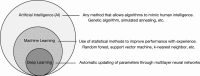
Artificial intelligence (AI) has contributed substantially to the resolution of a variety of biomedical problems, including cancer, over the past decade. Deep learning, a subfield of AI that is highly flexible and supports automatic feature extraction, is increasingly being applied in various areas of both basic and clinical cancer research. In this review, we describe numerous recent examples of the application of AI in oncology, including cases in which deep learning has efficiently solved problems that were previously thought to be unsolvable, and we address obstacles that must be overcome before such application can become more widespread. We also highlight resources and datasets that can help harness the power of AI for cancer research. The development of innovative approaches to and applications of AI will yield important insights in oncology in the coming decade.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; machine learning; oncology; personalized medicine.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rajkomar A, Dean J, Kohane I. Machine learning in medicine. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1347‐1358. - PubMed
-
- LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521:436‐444. - PubMed
-
- Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016;316:2402‐2410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

