Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement Aided by a New Drill Guide Template Combined with Fluoroscopy: An Accuracy Study
- PMID: 32133781
- PMCID: PMC7189065
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12642
Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement Aided by a New Drill Guide Template Combined with Fluoroscopy: An Accuracy Study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the accuracy of percutaneous pedicle screw (PPS) placement aided by a new drill guide template.
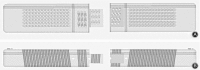
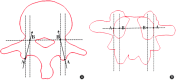
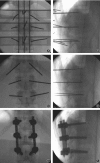
Methods: The patients were divided into guide template group and conventional perspective group. In the conventional perspective group, the screws were placed by hand under fluoroscopy. In the guide template group, the screw placement was aided by a new drill guide template, and the drill guide template is designed according to the patient's ideal pedicle screw, but not based on skin morphology. The accuracy was evaluated by comparing the following parameters between the two groups: pedicle breach level, inclination angle deviation between the left and right screws, sagittal angle deviation between the left and right screws, and position deviation of the left and right screw entry points. The consistency of the postoperative screw angle and the corresponding guide template inclination angle was compared in the guide template group. The operative time, blood loss, and radiation times were compared between the groups.
Results: A total of 146 patients (876 screws) were enrolled in our study including 79 (474 screws) in the guide template group and 67 (402 screws) in the conventional perspective group. The pedicle breach level in the guide template group (22/474) was significantly lower than that in the conventional perspective group (47/402) (P < 0.05). The position and direction deviations of the left and right screws in the guide template group (2.06 ± 1.02 mm, 1.23 ± 1.25 mm, 1.83° ± 1.49°) were significantly less than those in the conventional perspective group (5.33 ± 2.99 mm, 4.32 ± 3.25 mm, 2.87° ± 1.56°). The operation time, blood loss, and radiation times were significantly lower in the guide template group (80.49 ± 9.14 min, 50.42 ± 8.9 mL, 11.02 ± 2.44) than those in the conventional perspective group (108.1 ± 21.18 min, 71.7 ± 17.09 mL, 23.53 ± 4.54). There were no significant differences between the postoperative screw angle and the corresponding guide template angle in the guide template group.
Conclusion: PPS placement aided by a new drill guide template yielded higher screw accuracy and less operative time, blood loss, and radiation exposure than traditional screw placement.
Keywords: 3D printing technology; Minimally invasive spine surgery; Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation (PPS); Thoracolumbar fractures.
© 2020 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Chinese Orthopaedic Association and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Lee JK, Jang JW, Kim TW, Kim TS, Kim SH, Moon SJ. Percutaneous short‐segment pedicle screw placement without fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: is it effective? Comparative study with open short‐segment pedicle screw fixation with posterolateral fusion. Acta Neurochir, 2013, 155: 2305–2312. - PubMed
-
- Van de KE, Costa F, Van de PD, Schils F. A prospective multicenter registry on the accuracy of pedicle screw placement in the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral levels with the use of the O‐arm imaging system and StealthStation Navigation. Spine, 2012, 37: 1580–1587. - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Cho YS, Riew KD. Free hand pedicle screw placement in the thoracic spine: is it safe? Spine, 2004, 29: 333–342. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

