Analysis of genomic-length HBV sequences to determine genotype and subgenotype reference sequences
- PMID: 32134374
- PMCID: PMC7416611
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001387
Analysis of genomic-length HBV sequences to determine genotype and subgenotype reference sequences
Abstract
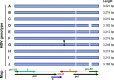
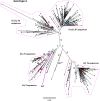
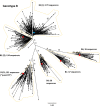
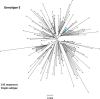
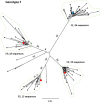
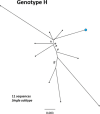
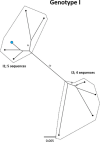
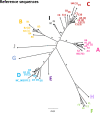
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a diverse, partially double-stranded DNA virus, with 9 genotypes (A-I), and a putative 10th genotype (J), characterized thus far. Given the broadening interest in HBV sequencing, there is an increasing requirement for a consistent, unified approach to HBV genotype and subgenotype classification. We set out to generate an updated resource of reference sequences using the diversity of all genomic-length HBV sequences available in public databases. We collated and aligned genomic-length HBV sequences from public databases and used maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis to identify genotype clusters. Within each genotype, we examined the phylogenetic support for currently defined subgenotypes, as well as identifying well-supported clades and deriving reference sequences for them. Based on the phylogenies generated, we present a comprehensive set of HBV reference sequences at the genotype and subgenotype level. All of the generated data, including the alignments, phylogenies and chosen reference sequences, are available online (https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.8851946) as a simple open-access resource.
Keywords: HBV; phylogenetics; reference sequences; whole genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

