A case of hyperkeratotic crusted scabies
- PMID: 32134911
- PMCID: PMC7058272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007918
A case of hyperkeratotic crusted scabies
Abstract
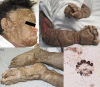
Patients who are immunocompromised or have cognitive or physical disabilities are at a higher risk of being affected with infections such as crusted scabies. This is a rare skin hyperinfestation by Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. The main characteristic of this dermatosis is a thick crust due to the high concentration of mites; in addition, other manifestations such as papules, excoriations, and burrows may be absent. In severe cases, thick yellow-brown crusts and plaques with deep fissures are present. Diagnosis can be made by observing mites, ova, or feces from skin scrapings. Multiple therapies can be used in patients with this condition. Management with patient isolation is important to prevent institutional outbreaks. This disease can have high mortality, primarily due to sepsis. Awareness of this condition and its serious consequences is important to reduce its mortality and morbidity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

