Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases
- PMID: 32138174
- PMCID: PMC7175224
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10030389
Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases
Abstract
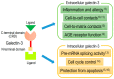
Galectin-3 is a β-galactoside-binding lectin which is important in numerous biological activities in various organs, including cell proliferation, apoptotic regulation, inflammation, fibrosis, and host defense. Galectin-3 is predominantly located in the cytoplasm and expressed on the cell surface, and then often secreted into biological fluids, like serum and urine. It is also released from injured cells and inflammatory cells under various pathological conditions. Many studies have revealed that galectin-3 plays an important role as a diagnostic or prognostic biomarker for certain types of heart disease, kidney disease, viral infection, autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and tumor formation. In particular, it has been recognized that galectin-3 is extremely useful for detecting many of these diseases in their early stages. The purpose of this article is to review and summarize the recent literature focusing on the biomarker characteristics and long-term outcome predictions of galectin-3, in not only patients with various types of diseases, but associated animal models.
Keywords: animal model; biomarker; diagnostic; early stage; galectin-3; prognostic; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical