Successful High-Dosage Monotherapy of Tigecycline in a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Pneumonia-Septicemia Model in Rats
- PMID: 32138210
- PMCID: PMC7148456
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9030109
Successful High-Dosage Monotherapy of Tigecycline in a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Pneumonia-Septicemia Model in Rats
Abstract
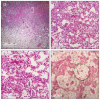
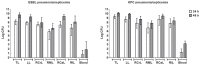
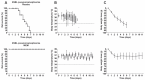
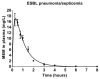
Background: Recent scientific reports on the use of high dose tigecycline monotherapy as a "drug of last resort" warrant further research into the use of this regimen for the treatment of severe multidrug-resistant, Gram-negative bacterial infections. In the current study, the therapeutic efficacy of tigecycline monotherapy was investigated and compared to meropenem monotherapy in a newly developed rat model of fatal lobar pneumonia-septicemia. Methods: A Klebsiella pneumoniae producing extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) and an isogenic variant producing K. pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) were used in the study. Both strains were tested for their in vitro antibiotic susceptibility and used to induce pneumonia-septicemia in rats, which was characterized using disease progression parameters. Therapy with tigecycline or meropenem was initiated at the moment that rats suffered from progressive infection and was administered 12-hourly over 10 days. The pharmacokinetics of meropenem were determined in infected rats. Results: In rats with ESBL pneumonia-septicemia, the minimum dosage of meropenem achieving survival of all rats was 25 mg/kg/day. However, in rats with KPC pneumonia-septicemia, this meropenem dosage was unsuccessful. In contrast, all rats with KPC pneumonia-septicemia were successfully cured by administration of high-dose tigecycline monotherapy of 25 mg/kg/day (i.e., the minimum tigecycline dosage achieving 100% survival of rats with ESBL pneumonia-septicemia in a previous study). Conclusions: The current study supports recent literature recommending high-dose tigecycline as a last resort regimen for the treatment of severe multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. The use of ESBL- and KPC-producing K. pneumoniae strains in the current rat model of pneumonia-septicemia enables further investigation, helping provide supporting data for follow-up clinical trials in patients suffering from severe multidrug-resistant bacterial respiratory infections.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; antibiotic resistance; meropenem; pneumonia; septicemia; tigecycline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative serum bactericidal activity of meropenem-based combination regimens against extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Oct;38(10):1925-1931. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03628-6. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31278562
-
Nosocomial blood-stream infections from extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia from GB Pant Hospital, New Delhi.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2010 Sep 3;4(8):517-20. doi: 10.3855/jidc.668. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2010. PMID: 20818104
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
-
The tigecycline evaluation and surveillance trial; assessment of the activity of tigecycline and other selected antibiotics against gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens from France collected between 2004 and 2016.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018 May 30;7:68. doi: 10.1186/s13756-018-0360-y. eCollection 2018. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018. PMID: 29876099 Free PMC article.
-
Imipenem-Relebactam and Meropenem-Vaborbactam: Two Novel Carbapenem-β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations.Drugs. 2018 Jan;78(1):65-98. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0851-9. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29230684 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Peptides Epinecidin-1 and Beta-Defesin-3 Are Effective against a Broad Spectrum of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Isolates and Increase Survival Rate in Experimental Sepsis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 9;11(1):76. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010076. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052952 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Flow Imaging Combined with Serum CRP, PCT, and IL-6 Levels for Neonatal Pneumonia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 10;2022:2113856. doi: 10.1155/2022/2113856. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9842065. doi: 10.1155/2023/9842065. PMID: 35990828 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Novel Antimicrobial Peptide AA139-Nanomedicines in a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Pneumonia-Septicemia Model in Rats.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Aug 20;64(9):e00517-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00517-20. Print 2020 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32540976 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of Klebsiella pneumoniae mucosal infections.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1367422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1367422. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38559342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topical adjunctive treatment with flagellin augments pulmonary neutrophil responses and reduces bacterial dissemination in multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1450486. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1450486. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duin D., Cober E.D., Richter S.S., Perez F., Cline M., Kaye K.S., Kalayjian R.C., Salata R.A., Evans S.R., Fowler V.G. Tigecycline therapy for carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) bacteriuria leads to tigecycline resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014;20:O1117–O1120. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12714. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

