Arabidopsis RETICULON-LIKE4 (RTNLB4) Protein Participates in Agrobacterium Infection and VirB2 Peptide-Induced Plant Defense Response
- PMID: 32138311
- PMCID: PMC7084338
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051722
Arabidopsis RETICULON-LIKE4 (RTNLB4) Protein Participates in Agrobacterium Infection and VirB2 Peptide-Induced Plant Defense Response
Abstract
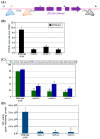
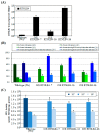
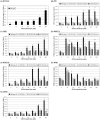
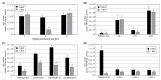
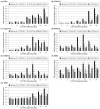
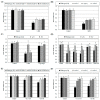
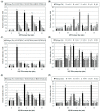
Agrobacterium tumefaciens uses the type IV secretion system, which consists of VirB1-B11 and VirD4 proteins, to deliver effectors into plant cells. The effectors manipulate plant proteins to assist in T-DNA transfer, integration, and expression in plant cells. The Arabidopsis reticulon-like (RTNLB) proteins are located in the endoplasmic reticulum and are involved in endomembrane trafficking in plant cells. The rtnlb4 mutants were recalcitrant to A. tumefaciens infection, but overexpression of RTNLB4 in transgenic plants resulted in hypersusceptibility to A. tumefaciens transformation, which suggests the involvement of RTNLB4 in A. tumefaciens infection. The expression of defense-related genes, including FRK1, PR1, WRKY22, and WRKY29, were less induced in RTNLB4 overexpression (O/E) transgenic plants after A. tumefaciens elf18 peptide treatment. Pretreatment with elf18 peptide decreased Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression efficiency more in wild-type seedlings than RTNLB4 O/E transgenic plants, which suggests that the induced defense responses in RTNLB4 O/E transgenic plants might be affected after bacterial elicitor treatments. Similarly, A. tumefaciens VirB2 peptide pretreatment reduced transient T-DNA expression in wild-type seedlings to a greater extent than in RTNLB4 O/E transgenic seedlings. Furthermore, the VirB2 peptides induced FRK1, WRKY22, and WRKY29 gene expression in wild-type seedlings but not efr-1 and bak1 mutants. The induced defense-related gene expression was lower in RTNLB4 O/E transgenic plants than wild-type seedlings after VirB2 peptide treatment. These data suggest that RTNLB4 may participate in elf18 and VirB2 peptide-induced defense responses and may therefore affect the A. tumefaciens infection process.
Keywords: Agrobacterium; RTNLB; VirB2; plant defense response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis RETICULON-LIKE3 (RTNLB3) and RTNLB8 Participate in Agrobacterium-Mediated Plant Transformation.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 24;19(2):638. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020638. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29495267 Free PMC article.
-
Plant proteins that interact with VirB2, the Agrobacterium tumefaciens pilin protein, mediate plant transformation.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):3148-67. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026476. Epub 2004 Oct 19. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15494553 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis RAB8A, RAB8B and RAB8D Proteins Interact with Several RTNLB Proteins and are Involved in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Infection Process.Plant Cell Physiol. 2021 Dec 3;62(10):1572-1588. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcab112. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34255832
-
Arabidopsis thaliana floral dip transformation method.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;343:87-103. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-130-4:87. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988336 Review.
-
Assembly of the VirB transport complex for DNA transfer from Agrobacterium tumefaciens to plant cells.Curr Opin Microbiol. 1998 Dec;1(6):649-55. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(98)80110-0. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 10066547 Review.
Cited by
-
A Plant Endophytic Bacterium Priestia megaterium StrainBP-R2 Isolated from the Halophyte Bolboschoenus planiculmis Enhances Plant Growth under Salt and Drought Stresses.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 17;10(10):2047. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102047. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296323 Free PMC article.
-
Agrobacterium tumefaciens: A Bacterium Primed for Synthetic Biology.Biodes Res. 2020 May 26;2020:8189219. doi: 10.34133/2020/8189219. eCollection 2020. Biodes Res. 2020. PMID: 37849895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide transcriptome and gene family analysis reveal candidate genes associated with potassium uptake of maize colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Sep 6;24(1):838. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05398-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39242995 Free PMC article.
-
A plant endophytic bacterium Burkholderia seminalis strain 869T2 increases plant growth under salt stress by affecting several phytohormone response pathways.Bot Stud. 2025 Feb 4;66(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40529-025-00453-3. Bot Stud. 2025. PMID: 39904843 Free PMC article.
-
Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase 1 mediates G3P accumulation for Eureka lemon resistance to citrus yellow vein clearing virus.Hortic Res. 2024 Oct 11;12(1):uhae287. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae287. eCollection 2025 Jan. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 39882172 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

