BMI modified the association of current smoking with the incidence of hypertension in Chinese population: a 22-year cohort study
- PMID: 32138723
- PMCID: PMC7059703
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-8428-z
BMI modified the association of current smoking with the incidence of hypertension in Chinese population: a 22-year cohort study
Abstract
Background: There was little known on how the interaction effect between obesity and current smoking affected the incidence of hypertension. The aim of this study was to investigate how body mass index (BMI) modified the effect of current smoking on the incidence of hypertension.
Methods: Data were obtained from the China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). According to the WHO recommendations for Chinese people, the normal weight, overweight, and obesity were defined using the BMI cutoff values 18.5 kg/m2, 23.0 kg/m2, and 27.5 kg/m, respectively. Current smokers were defined as having smoked at least 100 cigarettes or electronic cigarettes, 20 cigars, or 20 tobacco pipes and other type of tobacco in the last 30 days preceding the survey. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure (SBP)/ diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥ 140/90 mmHg, use of anti-hypertensive medications, or a self-reported diagnosis.
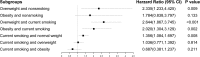
Results: This study included 12,900 subjects. There were interaction effects between obesity and current smoking in females (P = 0.030) and the 50-59 years group (P = 0.049). Current smoking was a significant predictor of incident hypertension only in the total and female populations with normal weight (HR: 1.119 and 1.274; HR 95% CI: 1.013-1.236 and 1.143-1.415; and P = 0.027 and 0.040, respectively). Stratified by age, current smoking affected the development of hypertension only in the 50-59 years subjects with the normal weight (HR: 1.356; HR 95% CI: 1.084-1.697; and P = 0.008).
Conclusions: Current smoking was a significant predictor of incident hypertension only in the female and middle-age populations with normal weight but not in the overweight and obesity as well as the younger and elder populations.
Keywords: Current smoking; Obesity; The incidence of hypertension; The interaction effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Body mass index and cancer incidence:a prospective cohort study in northern China].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;35(3):231-6. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24831616 Chinese.
-
Total and abdominal obesity among rural Chinese women and the association with hypertension.Nutrition. 2012 Jan;28(1):46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 May 31. Nutrition. 2012. PMID: 21621392
-
[Body mass index and the risk of lung cancer incidence in smokers: a prospective cohort study].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 May;50(5):385-90. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.05.001. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27141892 Chinese.
-
[Trajectories of body mass index and risk of hypertension and blood pressure among Chinese adults].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2023 May;52(3):354-361. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2023.03.002. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37500512 Chinese.
-
The association between amount of cigarettes smoked and overweight, central obesity among Chinese adults in Nanjing, China.Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16(2):240-7. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17468078
Cited by
-
Early-onset alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drug use with age at onset of hypertension: a survival analysis.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2024 Jul;59(7):1129-1141. doi: 10.1007/s00127-023-02596-9. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38104055
-
Effectiveness of the knowledge, attitude, practice intervention model in the management of hypertension in the elderly.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 May;26(5):465-473. doi: 10.1111/jch.14770. Epub 2024 Mar 11. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 38468407 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of smoking intensity trajectory, cumulative smoking exposure, and the number of years since quitting on the subsequent risk of hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022 Jul;24(7):937-944. doi: 10.1111/jch.14534. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022. PMID: 35765239 Free PMC article.
-
Dawning public health services dogma: An indigenous Southwest Chinese perspective in managing hypertension-with or without the "BPHS"?Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 10;10:1017795. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1017795. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36438225 Free PMC article.
-
Safety, efficacy and airway complications of the flexible laryngeal mask airway in functional endoscopic sinus surgery: A retrospective study of 6661 patients.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0245521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245521. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33539365 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical