P-selectin blockade ameliorates lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice through improving renal hypoxia and evaluation using BOLD-MRI
- PMID: 32138730
- PMCID: PMC7059679
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02284-1
P-selectin blockade ameliorates lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice through improving renal hypoxia and evaluation using BOLD-MRI
Abstract
Background: Lupus nephritis is one of the most common and severe complications of systemic lupus erythematosus, of which poor prognosis is indicated by aggravated renal hypoxia and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Cell adhesion molecules play a key role in the progression of lupus nephritis tubulointerstitial lesion, including P-selectin, which mediates the rolling of leukocytes and subsequent adhesion and infiltration and then initiates the inflammatory immune response and ischemia and hypoxia injury. However, the effects and mechanisms of P-selectin in lupus nephritis remain to be investigated, and a noninvasive measurement of lupus nephritis tubulointerstitial hypoxia and fibrosis remains to be explored.
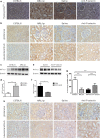
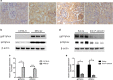
Methods: Thirty-four MRL/lpr mice were randomly divided into the following three groups: MRL/lpr, saline, and anti-P-selectin, which consisted of no treatment, treatment with normal saline, and treatment with anti-P-selectin monoclonal antibody (mAb) from 12 to 16 weeks of age, respectively. Ten male C57BL/6 mice of the same age served as normal controls. 24-h urinary protein, urinary albumin-creatinine ratio, and periodic acid-Schiff were used to assess kidney damage; Western blot or immunohistochemical staining of the hypoxia probe Hypoxyprobe™-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), and CD31 were used to evaluate hypoxia in renal tissue; and NADPH oxidase subunit gp91phox and p22phox were used to examine renal oxidative stress. The correlation between kidney injury and blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-MRI) was calculated to assess the clinical value of BOLD-MRI.
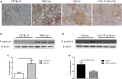
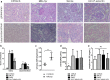
Results: P-selectin is upregulated in lupus nephritis. Blocking P-selectin with mAb alleviated renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis, renal hypoxia, and peritubular capillary loss, without alteration of the levels of lupus activity indicators, anti-dsDNA antibody, or complement C3. BOLD-MRI showed that the reduced R2* values in the renal cortex and medulla of lupus mice were increased when treated with anti-P-selectin mAb as compared with those treated with normal saline, which were negatively correlated with Hypoxyprobe™-1 hypoxia probe and the expression of HIF-1α.
Conclusions: Early intervention of lupus nephritis with anti-P-selectin mAb can significantly improve the hypoxic state of the kidney and reduce the severity of tubulointerstitial lesions. BOLD-MRI techniques are noninvasive and can dynamically evaluate the changes in renal lesions and intrarenal oxygenation levels before and after treatment in lupus nephritis.
Keywords: BOLD-MRI; Hypoxic; Lupus nephritis; Tubulointerstitial fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complement factor B inhibitor LNP023 improves lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113433. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113433. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36076550
-
Microthrombotic Renal Vascular Lesions Are Associated to Increased Renal Inflammatory Infiltration in Murine Lupus Nephritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 28;9:1948. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01948. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30210500 Free PMC article.
-
The new complement inhibitor CRIg/FH ameliorates lupus nephritis in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Nov 21;20(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1599-0. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31752725 Free PMC article.
-
Renal tubulointerstitial hypoxia: cause and consequence of kidney dysfunction.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011 Jul;38(7):474-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05532.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21545630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the understanding of renal inflammation and fibrosis in lupus nephritis.F1000Res. 2017 Jun 13;6:874. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.10445.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28663794 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway.Open Life Sci. 2023 Jul 17;18(1):20220649. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0649. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37483429 Free PMC article.
-
Shen Shuai II recipe improves renal hypoxia to attenuate renal injury in 5/6 renal ablation/infarction rats and effect evaluation using blood oxygenation level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2338565. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2338565. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38622926 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering 3D-BMSC exosome-based hydrogels that collaboratively regulate bone microenvironment and promote osteogenesis for enhanced cell-free bone regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2025 May 20;32:101881. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101881. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40510837 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion molecules: a way to understand lupus.Reumatologia. 2022;60(2):133-141. doi: 10.5114/reum.2022.115664. Epub 2022 May 18. Reumatologia. 2022. PMID: 35782027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SELP, CD93, IL2RG, and VAV1 Genes Associated with Atherosclerosis May Be Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Psoriasis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Feb 27;16:827-843. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S398862. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36876153 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

