Role of Proinsulin Self-Association in Mutant INS Gene-Induced Diabetes of Youth
- PMID: 32139596
- PMCID: PMC7171958
- DOI: 10.2337/db19-1106
Role of Proinsulin Self-Association in Mutant INS Gene-Induced Diabetes of Youth
Abstract
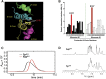
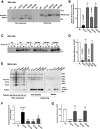
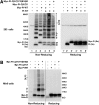
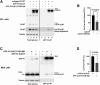
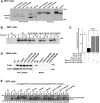
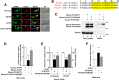
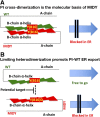
Abnormal interactions between misfolded mutant and wild-type (WT) proinsulin (PI) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) drive the molecular pathogenesis of mutant INS gene-induced diabetes of youth (MIDY). How these abnormal interactions are initiated remains unknown. Normally, PI-WT dimerizes in the ER. Here, we suggest that the normal PI-PI contact surface, involving the B-chain, contributes to dominant-negative effects of misfolded MIDY mutants. Specifically, we find that PI B-chain tyrosine-16 (Tyr-B16), which is a key residue in normal PI dimerization, helps confer dominant-negative behavior of MIDY mutant PI-C(A7)Y. Substitutions of Tyr-B16 with either Ala, Asp, or Pro in PI-C(A7)Y decrease the abnormal interactions between the MIDY mutant and PI-WT, rescuing PI-WT export, limiting ER stress, and increasing insulin production in β-cells and human islets. This study reveals the first evidence indicating that noncovalent PI-PI contact initiates dominant-negative behavior of misfolded PI, pointing to a novel therapeutic target to enhance PI-WT export and increase insulin production.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Edghill EL, Flanagan SE, Patch A-M, et al. .; Neonatal Diabetes International Collaborative Group . Insulin mutation screening in 1,044 patients with diabetes: mutations in the INS gene are a common cause of neonatal diabetes but a rare cause of diabetes diagnosed in childhood or adulthood. Diabetes 2008;57:1034–1042 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

